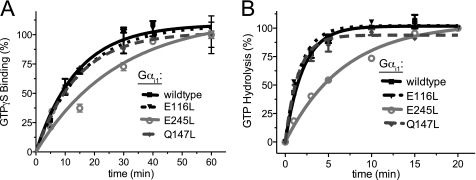
FIGURE 4.
Rates of guanine nucleotide binding and hydrolysis by affinity-enhanced Gαi1 mutants. A, nucleotide binding assays were initiated by the addition of [35S]GTPγS to 100 nm WT or mutant Gαi1 protein in either assay buffer or nonspecific buffer (the latter with excess unlabeled nucleotide). At the indicated time points, 100 μl of the protein mixture was vacuum-filtered through nitrocellulose, washed four times, and counted by scintillation. Assays were conducted in duplicate. The error bars represent S.E. Rates of binding (kobs) were determined using nonlinear regression to be 0.07 min−1 (95% CI, 0.04–0.10), 0.04 min−1 (95% CI, 0.02–0.05), 0.06 min−1 (95% CI, 0.04–0.09), and 0.07 min−1 (95% CI, 0.06–0.08) for Gαi1WT, Gαi1E245L, Gαi1E116L, and Gαi1Q147L, respectively. B, intrinsic GTPase activities of WT and mutant Gαi1 subunits were determined using [γ-32P]GTP single-turnover assays. 100 nm Gαi1 protein was loaded with [γ-32P]GTP at 20 °C for 10 min before assays were initiated by the addition of Mg2+ (10 mm) and GTPγS (400 μm). At the indicated time points, 100 μl of the protein mixture was quenched with activated charcoal, and released [32P]Pi was counted by scintillation. Assays were conducted in duplicate. The error bars represent S.E. GTPase rates (kcat) were determined using nonlinear regression to be 0.48 min−1 (95% CI, 0.40–0.56), 0.15 min−1 (95% CI, 0.12–0.17), 0.58 min−1 (95% CI, 0.46–0.70), and 0.65 min−1 (95% CI, 0.50–0.81) for Gαi1WT, Gαi1E245L, Gαi1E116L, and Gαi1Q147L, respectively.