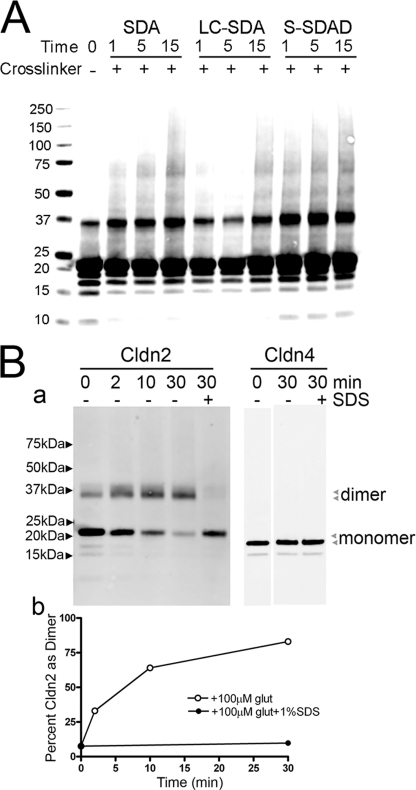
FIGURE 2.
Chemical cross-linking of cldn2 results in formation of dimers but not higher molecular weight forms. A, His-tagged cldn2 was extracted from induced MDCK II cells with 1% DDM and purified on Talon resin and cross-linked using photoactivated cross-linkers, electrophoresed using SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with cldn2 antibody. Some SDS-resistant cldn2 dimer is evident in the absence of cross-linker (−); addition of three cross-linkers of different lengths all resulted in an increase in dimer formation with only minor increases in higher molecular weight bands. Water-insoluble SDA and NHS-LC-diazirine showed time-dependent increases in cross-linking (1, 5, and 15 min), whereas water-soluble S-SDAD showed maximal cross-linking at shortest period (1 min) of UV exposure; in no case was cross-linked cld2 more than 20% of monomeric cldn2. B, His-tagged cldn2 and cldn4 were purified as described above and cross-linked by incubation with glutaraldehyde for 0–30 min; 1% SDS was added to some samples to disrupt oligomerization. Panel a, cross-linking to dimer is evident for cldn2 (left panel) but not cldn4 (right panel) in the absence (−) but not the presence (+) of SDS; the positions of monomers and dimers for cldn2 and cldn4 are indicated by arrowheads. Panel b, conversion to dimer is quantified by densitometry of the immunoblots in (panel a).