FIGURE 3.
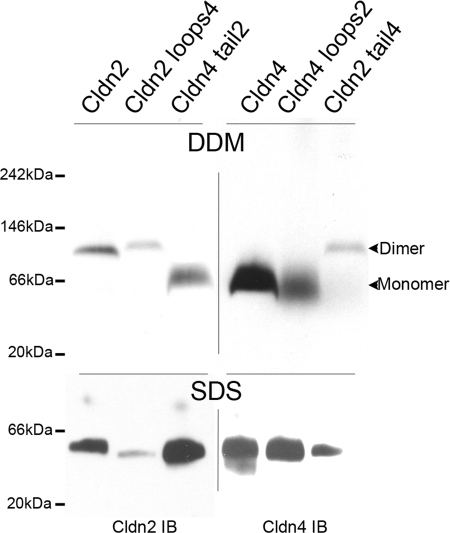
Dimerization of cldn2 is not mediated through its extracellular domains or its cytoplasmic carboxyl-terminal domain. Top left panel, stably transfected MDCK II Tet-Off cells induced to express wild-type cldn2, chimeric cld2 with the extracellular domains of cldn4 (cldn2 loops4), or cld4 with the cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus of cldn2 (cldn4 tail2) were extracted with DDM, electrophoresed in BN-PAGE, and immunoblotted for cldn2. cldn2 and cldn2 loops4 migrate as dimers, whereas cld4 tail 2 migrates in a broad band consistent with monomer. Top right panel, cells expressing wild-type cldn4, cldn4 loops 2, and cldn2 tail4 were similarly processed but immunoblotted for cldn4; cldn4 and cldn4 loops2 migrate as broad band in the range of monomers, whereas cldn2 tail4 migrates as a dimer. Bottom panels, treatment of DDM-extracted claudins and chimeras with 1% SDS results in similar electrophoretic mobility for all transgenes.