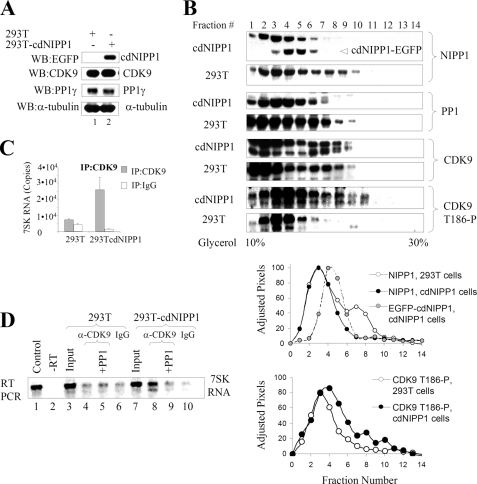
FIGURE 1.
Effect of cdNIPP1 expression on NIPP1 distribution, CDK9 phosphorylation, and association with 7SK RNA. A, analysis of 293T-cdNIPP1 cells is shown. Western blot analysis of 293T and 293T-cdNIPP1 cells with antibodies for EGFP (to check for the expression of cdNIPP1-EGFP), CDK9, PP1γ, and α-tubulin is shown. B, expression of cdNIPP1 changes NIPP1 distribution and increases CDK9 phosphorylation on Thr186. Whole cell extracts were prepared from 293T and 293T-cdNIPP1 cells and separated on glycerol gradients by ultracentrifugation. The gradients were fractionated and analyzed by Western blotting for NIPP1, PP1, CDK9, and CDK9 phosphorylated on Thr186. The NIPP1 and CDK9 phosphorylated on Thr186 immunoblots were scanned and quantified using PhosphorImager OptiQuant software. The pixels were adjusted to have the same total amount for the 293T and the cdNIPP1 extracts, and the normalized results are graphed (lower panels). C, expression of cdNIPP1 increases the association of CDK9 with 7SK RNA. RNA was isolated from material that co-precipitated with CDK9 from 239T or 293T-cdNIPP1 whole cell lysates. The RNA was reverse transcribed and analyzed by real time PCR. Results are presented as numbers of copies of 7SK RNA. D, PP1 removes CDK9-associated 7SK RNA. RNA was isolated from material that co-immunoprecipitated with CDK9 from 239T or 293T-cdNIPP1 cells, reverse-transcribed, and analyzed by semiquantitative PCR (26 cycles) using 7SK-specific primers. Lane 1, control using 7SK expression vector. Lane 2, control that was not reverse-transcribed. Lanes 3 and 7 are inputs. Lanes 4 and 8, 7SK RNA associated with CDK9 in 293T or 293T-cdNIPP1 whole cell lysates. Lanes 5 and 9, immunoprecipitated CDK9 was treated with purified rabbit muscular PP1C prior to the RNA extraction. Lanes 6 and 10, controls in which the immunoprecipitations were carried out with nonspecific rabbit IgG.