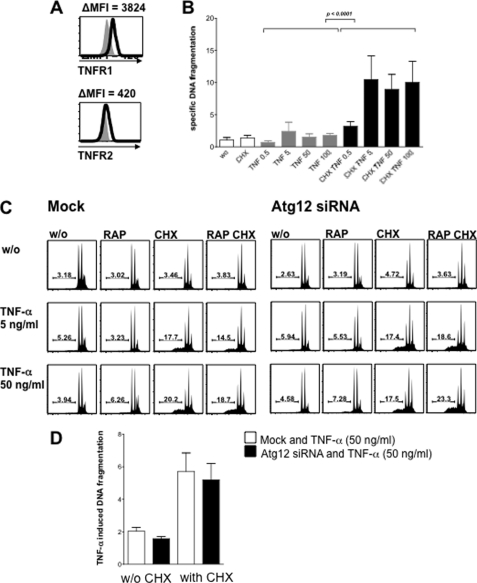
FIGURE 6.
Resistance of skeletal muscle cells to TNF-α-induced cell death. A, TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 are expressed on the surface of CCL136 muscle cells. B, CCL136 skeletal muscle cells are resistant to TNF-α treatment alone but showed a dose-dependent induction of cell death in the presence of TNF-α and the protein synthesis inhibitor CHX (1 μg/ml). Apoptotic cell death was analyzed after 24 h by quantifying TO-PRO-3 permeability and specific DNA fragmentation in hypodiploid cells. C, macroautophagy function does not interfere with susceptibility to TNF-receptor-mediated cell death in human CCL136 muscle cells. Neither loss of macroautophagic function due to atg12-specific RNA interference nor gain of macroautophagy function by mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition due to rapamycin treatment (RAP, 1 μg/ml) showed any effect on specific DNA fragmentation levels following TNF-α treatment. D, quantification of TNF-α-induced DNA fragmentation in CLL136 cells treated with or without atg12-specific RNA in the presence or absence of CHX averaged from seven independent experiments. Specific DNA fragmentation was compared using the paired t test.