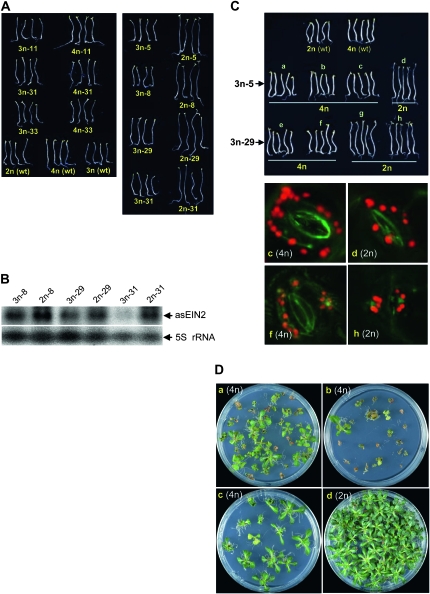
Figure 7.—
Assay for EIN2 silencing induced by the EIN2 antisense construct (asEIN2). (A) EIN2 silencing in F1 3n plants and their parental 4n (left) or 2n lines (right). Within each panel the plants on the left are 3n lines and those on the right the 4n or 2n parental lines. Seed was plated on MS medium containing ACC and allowed to germinate in darkness. Five seedlings from each line were then photographed. Longer hypocotyls in comparison to wild-type Arabidopsis indicate EIN2 silencing. (B) Northern blot hybridization detection of EIN2 antisense RNAs in three of the 3n lines and their 2n parental lines. (C) EIN2 silencing in 4n and 2n progeny derived from two of the 3n lines, 3n-5 and 3n-29. Only the 2n progeny displayed observable EIN2 silencing. The ploidy level was confirmed by visualization of chloroplasts in the leaf guard cells (lower). (D) Hygromycin sensitivity of offspring from 3n-5 plants in C. A large proportion of seedlings of the 4n progeny lines a and b shown in C died or showed little growth on medium containing 20 mg/liter of hygromycin, indicating silencing of the hygromycin resistance selectable marker gene in the asEIN2 transgene. This is in contrast to the seedlings of the 2n progeny line d derived from the same 3n parent, which showed vigorous growth on hygromycin medium, indicating active expression of the selectable marker gene.