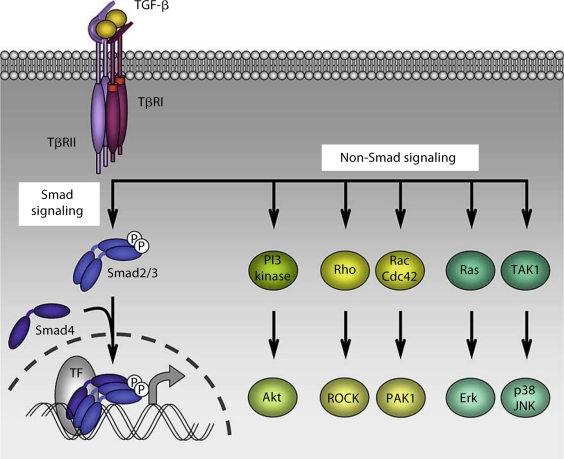
Fig. 2.
Smad and non-Smad signaling in TGF-β-induced EMT. TGF-β initiates signaling through 2 pairs of dual specificity kinase receptors that activate the intracellular signal transducers Smad2 and Smad3 through direct C-terminal phosphorylation. Following activation, Smad2 and Smad3 combine with Smad4, and these trimeric complexes then translocate into the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes through interaction with DNA-binding transcription factors (TF), coactivators and corepressors. In addition, TGF-β initiates non-Smad signaling pathways such as PI3 kinase-Akt, Rho-like GTPases and MAP kinase pathways. Both Smad and non-Smad signaling pathways are involved in TGF-β-induced EMT responses.