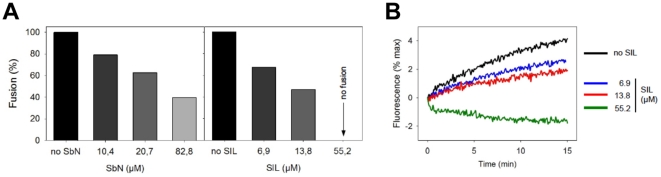
Figure 3. Silibinin and SIL inhibit HCVpp-mediated fusion.
Membrane fusion between HCVpp and R18-labeled liposomes was followed by fluorescence spectroscopy with excitation and emission at 560 and 590 nm, respectively. Fluorescent liposomes (12.5 µM final lipid concentration) were added to 20 µl of HCVpp in PBS pH 7.4 at 37°C, in the absence or presence of 5, 10 or 40 µg/ml of indicated compound, which corresponds to 6.9, 13.8 or 55 µM of SIL and 10.4, 20.7, and 82.8 µM of silibinin. After a 2 min-equilibration, lipid mixing was initiated by decreasing the pH to 5.0 with diluted HCl, and R18 dequenching was recorded. Maximal fluorescence was obtained after addition of 0.1% final Triton X-100 to the cuvette. A, values of the last min of fusion (final extent of fusion) were used to calculate the percentage of fusion in the presence of the drug, relative to 100% fusion in the absence of drug. Results are expressed from the mean of 2 separate experiments. Compounds were added at 5 (black), 10 (dark grey) or 40 µg/ml (light grey). B, fusion kinetics of HCVpp with liposomes, in the absence (black) or presence of three concentrations of SIL: blue, 5 µg/ml; red, 10 µg/ml and green, 40 µg/ml.