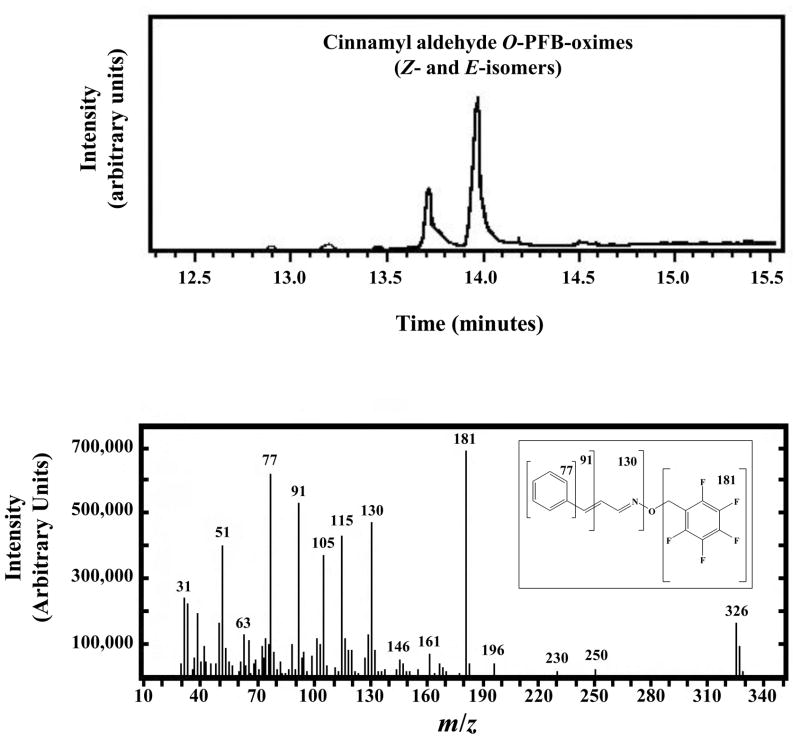
Figure 3. GC-MS Analysis of the ADH3-generated Cinnamyl Aldehyde.
Cinnamyl aldehyde was first generated enzymatically by treating cinnamyl alcohol with ADH3 as described in the legend to Figure 2. Cinnamyl aldehyde was converted to the perfluorobenzyl oxime (O-PFB-oxime) with PFBHA and analyzed by GC-MS. The resulting cinnamyl aldehyde O-PFB-oxime exists as the E- and Z-isomers, which have different retention times in the gas chromatograph (upper panel), but exhibit identical fragmentation patterns from the mass spectrometer (lower panel). The structure and fragmentation pattern of cinnamaldehyde O-perfluorobenzyl oxime are shown in the inset to the lower panel.