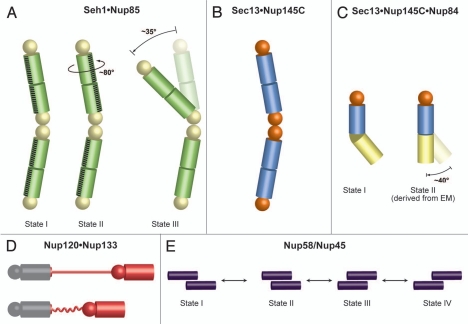
Figure 4.
Flexibility and dynamics of NPC components. Spheres represent β-propeller domains, while cylinders represent α-helical solenoid domains (A) Crystal structures of the Seh1•Nup85 hetero-octamer (yellow and green, respectively) in three different conformational states revealed a rotation and a hinge motion.35 (B) Sec13•Nup145C (orange and blue, respectively) forms a hetero-octamer.34 (C) Sec13•Nup145C•Nup84 (colored as in panel B, Nup84 in yellow) forms a subcomplex that matches a hinge observed in one conformation of the heptameric Nup84 complex as determined by EM.37 A straight arrangement of this trimer would correspond to the second conformation of this subcomplex as revealed by EM.40 Notably, the homodimerization and heterodimerization surfaces of Nup145C are overlapping and therefore promiscuous. (D) Nup133 binds to Nup120 via a short N-terminal segment at the end of an unstructured region.38 Since the two proteins are localized at opposite ends of the Nup84 complex, this finding suggests a head-to-tail arrangement of the heptamers. Contraction and expansion of the unstructured region may allow for the flexible tethering of Nup120 and Nup133. (E) Four different states of Nup58/Nup45 tetramers have been crystallographically observed.42 The sliding of two Nup58/Nup45 dimers (purple) alters the overall dimensions of the tetramer. Nup58/Nup45 refers to two alternatively spliced variants (Nup58 and Nup45) and the determined structure is common to both proteins.