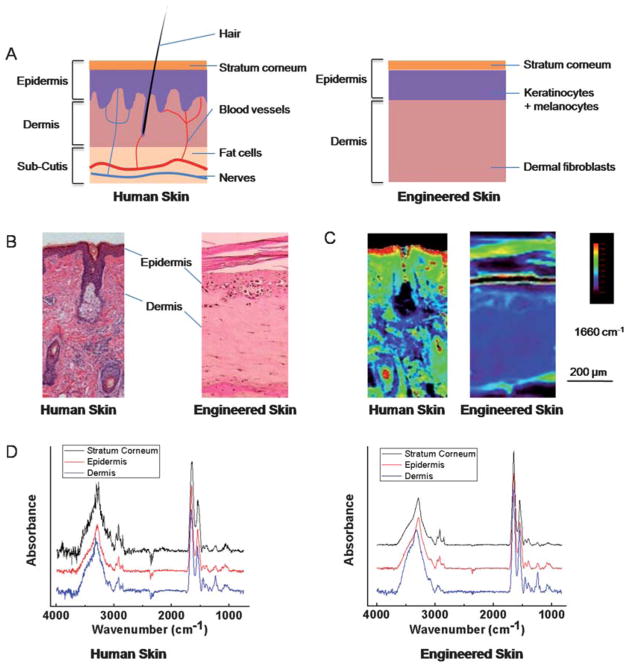
Fig. 1.
Skin structure and characterizations. (A) Schematic of human (left) and engineered skin (right). The epidermis is located at the skin-air interface while the dermis is located to the bottom of the image and contains various histologic structures. Engineered skin retains the most important components but does not contain accessory structures. (B) Histology of skin is usually deduced manually in tissue stained by Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E). Epidermis typically stains darker than dermis. (C) Infrared absorbance image from a corresponding serial section of the tissue at 1660 cm−1. Human skin was imaged on a low-e slide in reflectance mode, and engineered skin was imaged on a BaF2 substrate in transmission mode. (D) IR spectra of single pixels from epidermis, dermis and stratum corneum regions of human and engineered skin after piecewise linear baseline subtraction.