Abstract
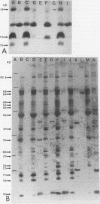
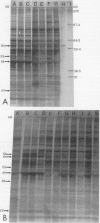
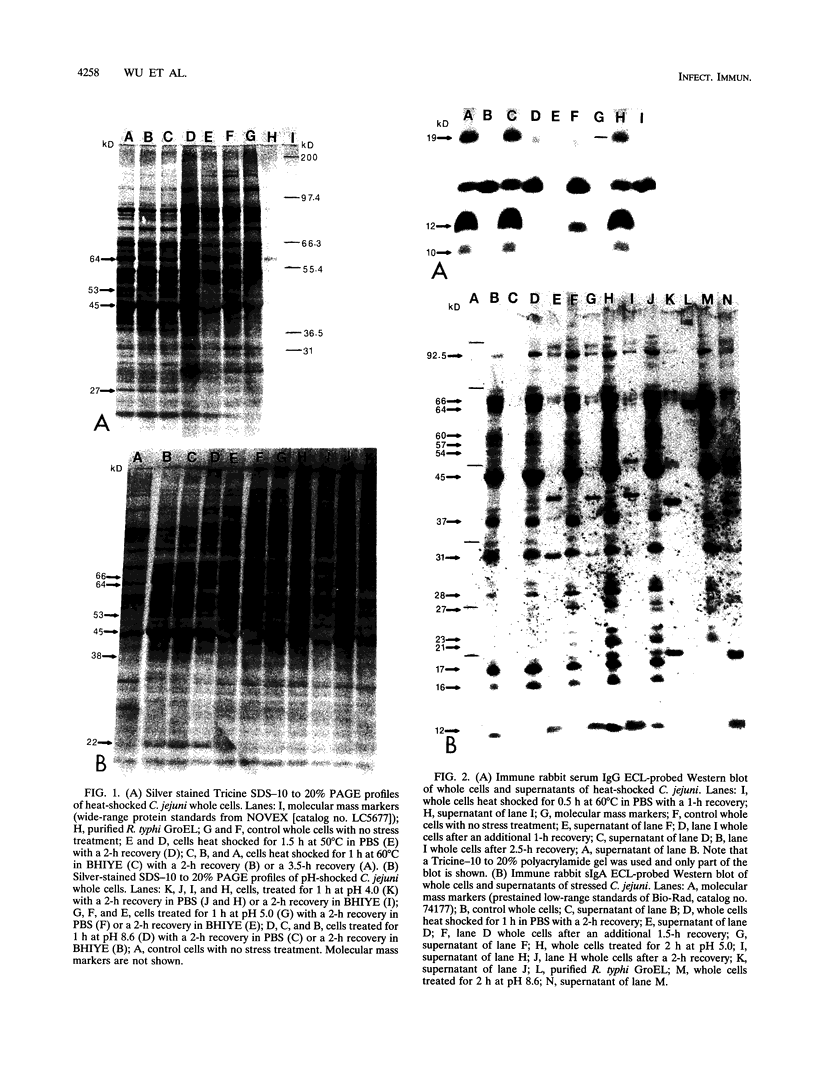
The protein response to physiological stress was characterized in Campylobacter jejuni 81176 after exposure to heat and pH shock and following periods of recovery. Immunoreactivities of major stress-related proteins were determined with anti-Campylobacter immune rabbit serum and intestinal lavage fluid. Distinct proteins with molecular masses ranging from 10 to 120 kDa were induced and/or released by selective heat or pH treatments. The most notable responses were those of two proteins with apparent molecular masses of 45 and 64 kDa that were induced and two other proteins of 10 and 12 kDa that were released by selective heat shock, alkaline pH treatment, or both. On the basis of N-terminal sequence analysis and immunological cross-reactivity data, the 64- and 10-kDa proteins were the C. jejuni homologs of Escherichia coli GroEL and GroES proteins, respectively. Enhanced chemiluminescence Western blotting (immunoblotting) revealed that all four proteins were among the major protein antigens recognized by anti-Campylobacter rabbit serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immune rabbit intestinal lavage IgA (secretory IgA). The results of this investigation suggest that the C. jejuni 10-, 12-, 45-, and 64-kDa proteins and a number of minor stress-related proteins deserve further evaluation of their respective roles in Campylobacter pathogenesis and immunity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangsborg J. M., Collins M. T., Høiby N., Hindersson P. Cloning and expression of the Legionella micdadei "common antigen" in Escherichia coli. APMIS. 1989 Jan;97(1):14–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett D. H., Chi E., Wright M. E. Sequence of the ompH gene from the deep-sea bacterium Photobacterium SS9. Gene. 1993 Sep 6;131(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90680-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr D. H., Kerner D. T., Blanco C. S., Bourgeois A. L., Wistar R., Jr Gastric lavage: a simple method to obtain IgA-rich intestinal secretions from the rabbit. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 20;99(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Walker R. I., Stewart S. D., Rogers J. E. Simple adult rabbit model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1176–1182. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1176-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czinn S. J., Cai A., Nedrud J. G. Protection of germ-free mice from infection by Helicobacter felis after active oral or passive IgA immunization. Vaccine. 1993;11(6):637–642. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90309-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNagel D. C., Pierce S. K. Heat shock proteins in immune responses. Crit Rev Immunol. 1993;13(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensgraber M., Loos M. A 66-kilodalton heat shock protein of Salmonella typhimurium is responsible for binding of the bacterium to intestinal mucus. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3072–3078. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3072-3078.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Engstrand L., Graham D. Y. Urease-associated heat shock protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2125–2127. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2125-2127.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. The emergence of the chaperone machines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Aug;17(8):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90439-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. L., Park R. W. Campylobacters associated with human diarrhoeal disease. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;69(3):281–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb01519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Alm R. A., Power M. E., Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Role of two flagellin genes in Campylobacter motility. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4757–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4757-4764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanteur D., Lakey J. H., Pattus F. The bacterial porin superfamily: sequence alignment and structure prediction. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2153–2164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Kabelitz D. Gamma/delta T lymphocytes and heat shock proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:191–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. M., Batchelor R. A., Bourgeois A. L., Burr D. H., Olson J. G. Urine and faecal IgA response during naturally acquired infection with Campylobacter jejuni. Lancet. 1987 May 16;1(8542):1141–1141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91694-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Neupert W. Heat shock proteins hsp60 and hsp70: their roles in folding, assembly and membrane translocation of proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:3–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathia D., Hoch G., Kievernagel Y. Influence of phytate on in vitro digestibility of casein under physiological conditions. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 1987;37(3):229–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01091787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Dertzbaugh M. T., Eldridge J. H., Hirasawa M., Kiyono H. The mucosal immune system: from fundamental concepts to vaccine development. Vaccine. 1992;10(2):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Bajardi A. C., Grisso C. L., Sieling P. A., Alland D., Convit J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A major T cell antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is a 10-kD heat-shock cognate protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):275–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. J., Young R. A. Stress and immunological recognition in host-pathogen interactions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4193–4196. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4193-4196.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Hart A. M. Western blot analysis of the human antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni cellular antigens during gastrointestinal infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):33–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.33-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport G. R. Heat shock proteins as vaccine candidates. Semin Immunol. 1991 Jan;3(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Anderson S. Proper and improper folding of proteins in the cellular environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:607–635. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi P., Losonsky G., DeTolla L. J., Morris J. G., Jr Human immune response to Campylobacter jejuni proteins expressed in vivo. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4938–4944. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4938-4944.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Rollins D. M., Haberberger R. L., Jr, Green A. E., Habash L., Strocko S., Walker R. I. Significance of flagella in colonization resistance of rabbits immunized with Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2259–2264. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2259-2264.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z. H., Ellison R. T., 3rd, Blaser M. J. Identification, purification, and characterization of major antigenic proteins of Campylobacter jejuni. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16363–16369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Weiss E. Biphasic culture system for rapid Campylobacter cultivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):284–289. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.284-289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. Heat shock proteins as antigens of bacterial and parasitic pathogens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:145–160. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglicht D., Padan E., Oppenheim A. B., Schuldiner S. An alkaline shift induces the heat shock response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):885–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.885-887.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J. How cells respond to stress. Sci Am. 1993 May;268(5):56–64. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0593-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J. Mammalian stress response: cell physiology, structure/function of stress proteins, and implications for medicine and disease. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4):1063–1081. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.4.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Jarjour W. N. Stress proteins, autoimmunity, and autoimmune disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;167:161–189. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75875-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor D. K., Jr, Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L. Western blot analysis of intestinal secretory immunoglobulin A response to Campylobacter jejuni antigens in patients with naturally acquired Campylobacter enteritis. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1217–1222. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano Y., Nishikawa T., Komatsu Y. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of anaerobically induced porin protein E1 (OprE) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilstra-Ryalls J., Fayet O., Georgopoulos C. The universally conserved GroE (Hsp60) chaperonins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:301–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]