Fig. 1.
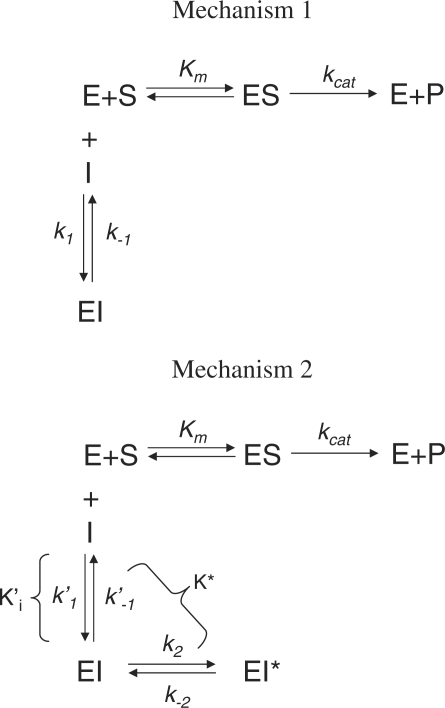
Enzyme inhibition mechanisms. In mechanism 1, the binding of inhibitor and isomerization of the complex are simultaneous and not distinguishable and therefore, k1 and k–1 represent the overall on-rate and off-rate constants. In mechanism 2, on the other hand, inhibition of enzyme occurs in two steps, characterized by the formation of a loose EI complex described by rate constants k′1 and k′–1 and isomerization of EI–EI* (the stable complex) occurs with an on-rate of k2 and an off-rate of k–2.