Fig. 5.
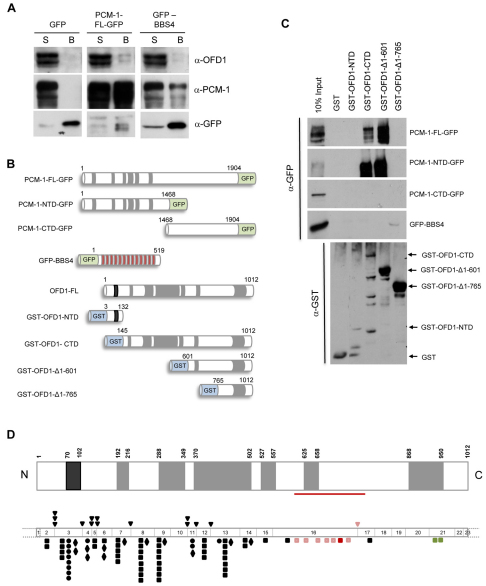
OFD1 and PCM-1 interact via their respective coiled-coil domains. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP alone, GFP-tagged full-length (FL) PCM-1 or GFP-tagged full-length BBS4. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GFP antibody, and both the unbound supernatant (S) and immunoprecipitates (bound, B) separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against OFD1, PCM-1 and GFP. (B) Schematic representation of GFP-tagged PCM-1 and BBS4 and GST-tagged OFD1 constructs used for interaction studies shown in C. Coiled-coil (grey), LisH (black) and TPR (red) motifs, as well as amino acid numbers, are indicated. (C) Purified GST alone or GST-tagged OFD1 constructs, as indicated, were incubated with lysates prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with PCM-1-GFP or GFP-BBS4 constructs. 10% of the input, together with the GST-bound material, were immunoblotted with an anti-GFP antibody. An anti-GST immunoblot shows the purified proteins in each fraction. (D) Schematic representation of OFD1 protein (upper diagram) is shown as in B, indicating the region (residues 601–765) essential for association with PCM-1 (red line). The lower diagram depicts the 23 exons of OFD1 gene drawn to scale so that the protein domains are aligned with their coding sequence. All point mutations identified to date are shown: frameshift (square), splice-site (triangle), nonsense (diamond) and missense (circle). Those found within the PCM-1-interacting region are shown in red and pink. The frameshift mutation in exon 16 depicted in red has been described in X-linked Simpson–Golabi–Behmel-like syndrome (Budny et al., 2006) and the frameshift mutations in exon 21 (green) have been described in an X-linked mental retardation syndrome with Joubert-like features (Coene et al., 2009). Full descriptions of mutations have been published (Macca and Franco, 2009).