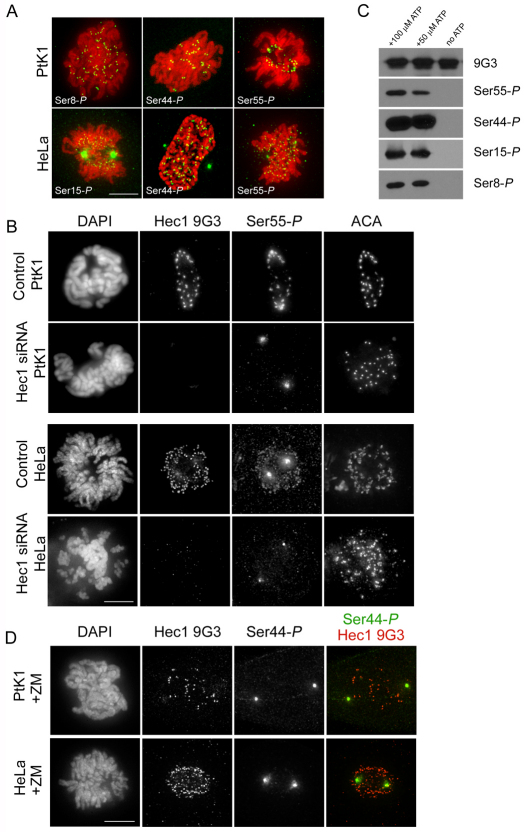
Fig. 3.
Hec1 is phosphorylated at kinetochores on multiple N-terminal serine residues and phosphorylation is dependent on Aurora B kinase. (A) Immunofluorescence images of PtK1 and HeLa cells stained with Hec1 phosphorylation-specific antibodies. Antibodies raised against peptides containing phosphorylated Ser8, Ser44 and Ser55 recognized kinetochores consistently in PtK1 cells, and antibodies raised against peptides containing phosphorylated Ser15, Ser44 and Ser55 recognized kinetochores consistently in HeLa cells. (B) Immunofluorescence images of mock-depleted or Hec1-depleted PtK1 and HeLa cells probed for Ser55-P. Kinetochore localization of the anti-Ser55-P antibody and the Hec1 9G3 antibody is lost upon depletion of Hec1. (C) Immunoblots of recombinantly expressed and purified NDC80Bonsai complexes probed with the non-phosphorylation-specific Hec1 9G3 antibody and the 4 phosphorylation-specific Hec1 antibodies. Purified NDC80Bonsai complexes were incubated with activated Aurora B kinase in the presence or absence of ATP and subjected to SDS-PAGE prior to immunoblot analysis. (D) Immunofluorescence images of a PtK1 and HeLa cell treated with 2 μM ZM447439. Kinetochore localization of Ser44-P is significantly diminished in both cell types in response to treatment with the inhibitor.