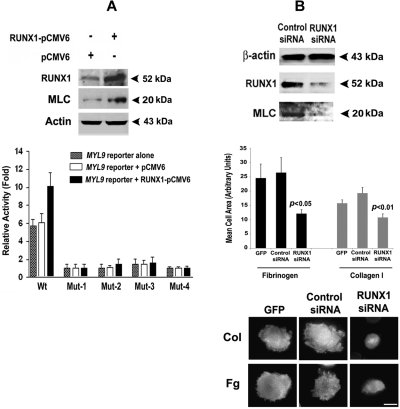
Figure 7.
Effect of overexpression of RUNX1 on expression of MLC protein and MYL9 promoter activity, and effect of RUNX1 siRNA on MLC protein and cell spreading in collagen and fibrinogen. (A) Immunoblot analysis of endogenous RUNX1, MLC, and actin after overexpression of RUNX1 in HEL cells (top panel). Effect of RUNX1 overexpression on MYL9 promoter activity (bottom panel). Wt and Mt constructs corresponding to sites I-IV were cotransfected with RUNX1-pCMV6 expression vector (black bars), empty vector pCMV6 (open bars), or neither (stippled bars) in HEL cells. Reporter activity was measured at 48 hours. Bar graphs show activity as mean (± S.E) of 3 independent experiments in triplicate. (B) Top panel: inhibition of MYL9 by RUNX1 siRNA. HEL cells were transfected with RUNX1 or mock siRNA. Shown are immunoblots of lysates for RUNX1, MLC, and β-actin, representative of 3 experiments. RUNX1 siRNA reduced endogenous RUNX1 and MLC protein expression. Middle and bottom panels: inhibition of cell spreading on collagen and fibrinogen by RUNX1 siRNA. Cells were transfected with GFP alone or with GFP and siRNA, as shown, and treated with PMA. Cell suspensions were seeded for 120 minutes on coverslips coated with either 50 μg/mL collagen I or 100 μg/mL fibrinogen. Adhered cells were fixed and labeled with rhodamine-phalloidin to decorate actin filaments. Cell spreading was measured as the mean cell surface area of at least 25 GFP-positive cells per sample, shown ± SEM. Spreading was significantly reduced (middle panel). P values show comparison to control siRNA. Cortical actin was absent (bottom panel) in RUNX1 knockdown cells exposed to collagen and fibrinogen. Bar in bottom panel, 10 mm.