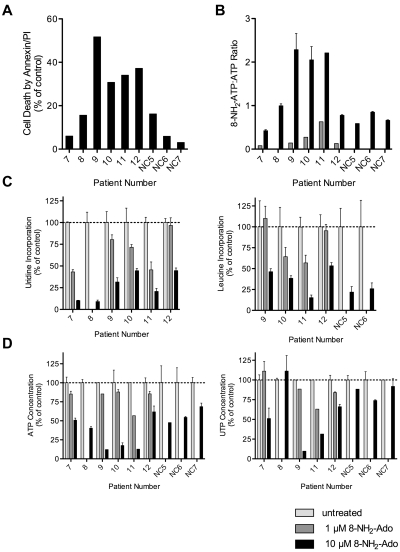
Figure 6.
Differential effects of 8-NH2-Ado on primary lymphoma cells and normal PBMCs. Freshly isolated cells were exposed to 1μM (gray bars) or 10μM (black bars) 8-NH2-Ado continuously for up to 48 hours. PBMC data from healthy donors are presented as controls. (A) Cell death by Annexin-V staining was normalized to untreated control cells. (B) The combined relative 8-NH2-Ado accumulation and ATP loss were represented by 8-NH2-ATP:ATP ratios. (C) Inhibition of transcription (left) and translation (right) was quantified by [3H]uridine and [3H]leucine incorporation. (D) The reduction in ATP (left) and UTP (right) levels were determined by HPLC analyses. When cell numbers were sufficient, independent experiments were performed in triplicate shown with SD error bars. All cells were incubated with 1 or 10μM 8-NH2-Ado for 48 hours in 10% human serum/RPMI with the following exceptions: patient 9 cells were incubated for 24 hours in 10% FBS/RPMI, and patient 12 cells were incubated for 24 hours. Patient numbers 7, 8, 9, and 12 were diagnosed with MCL. Patient 10 was diagnosed with marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, and patient 11 was diagnosed with splenic marginal zone B-cell lymphoma in transformation.