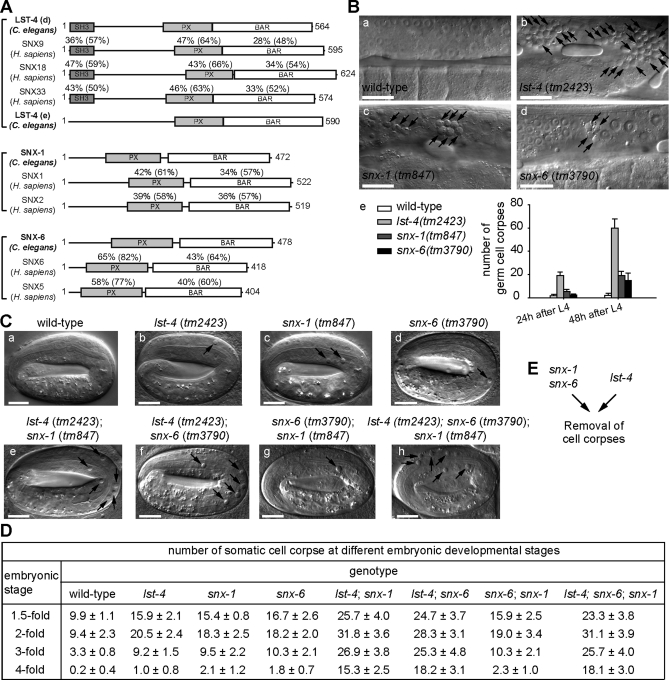
FIGURE 1:
Inactivation of lst-4, snx-1, and snx-6 results in the accumulation of apoptotic cells. (A) Domain structures of LST-4, SNX-1, SNX-6 and their mammalian orthologues. The percentage of amino acid identity (similarity in parentheses) of each domain between the C. elegans protein and each of its mammalian homologues are indicated. SH3: Src homology 3; PX: phox homology; BAR: Bin-amphiphysin-Rvs. (B) (a–d) DIC images of gonads of adult hermaphrodites at 48 h post-L4 stages. Arrows indicate cell corpses. Dorsal is to the top. Scale bars, 20 μm. (e) The number of germ cell corpses per gonad arm in adult hermaphrodites at 24 and 48 h post-L4 stage. Fifteen animals were scored for each datum. (C) DIC images of fourfold stage embryos with indicated genotypes. Arrows indicate persistent somatic cell corpses. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) The number of somatic cell corpses at different embryonic stages. At least 15 embryos were scored for each datum. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (E) Diagram illustrating that snx-1 and snx-6 act in one genetic pathway and lst-4 acts in another, as indicated by the results in (D).