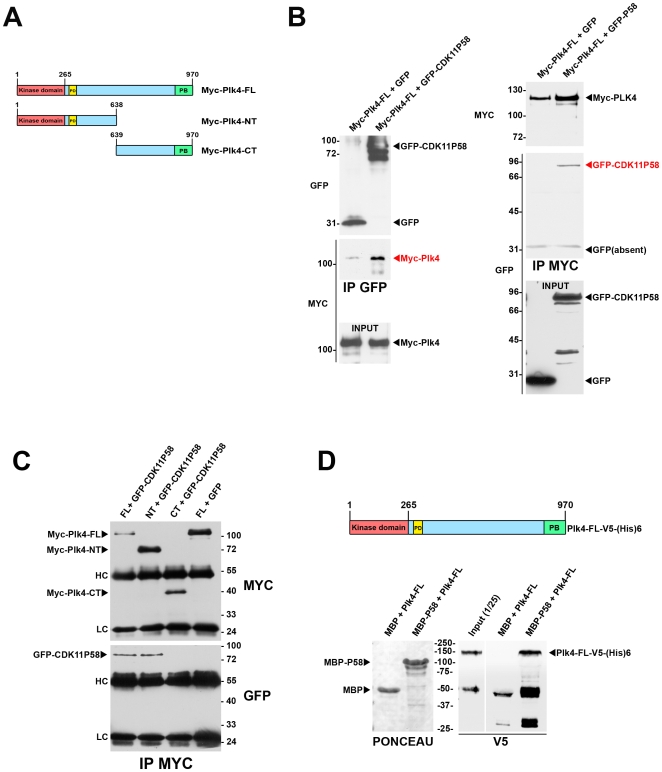
Figure 4. Plk4 and CDK11p58 can interact in vitro and in vivo.
A) Scheme of the different Plk4 constructs used for the co-transfection and immunoprecipitation experiments. Myc-Plk4-FL: Myc-tagged Plk4 full length; Myc-Plk4-NT: Myc-tagged Plk4 N-terminus domain; Myc-Plk4-CT: Myc-tagged Plk4 C-terminus domain. The catalytic domain (CD) is displayed in red, the polo box (PB) in green and the phosphodegron (PD) in yellow. B) GFP or GFP-CDK11p58 were co-transfected with Myc-Plk4 in COS7 cells and the proteins were immunoprecipitated using GFP (left) or Myc antibodies (right). Myc-Plk4 was co-immunoprecipitated with GFP-CDK11p58 but not with GFP (left). GFP-CDK11p58 (but not GFP) was also found in the Myc-Plk4 immunoprecipitates (right). C) Myc-Plk4-FL, Myc-Plk4-NT, Myc-Plk4-CT were co-transfected with GFP and/or GFP-CDK11p58 in COS7 cells. Myc-tagged Plk4 proteins were immunoprecipitated and revealed by Myc (top)(bottom). GFP-CDK11p58 is detected in Myc-Plk4-FL and NT immunoprecipitates whereas it is absent from Myc-Plk4-CT pull down (bottom). HC: immunoglobulin heavy chains; LC: immunoglobulin low chains. D) Maltose Binding proteins (MBP) or MBP-CDK11p58 proteins were immobilised on amylose beads and incubated with recombinant Plk4-V5-(His)6. After washes, the beads (and bound proteins) were boiled in Laemmli buffer and the proteins were analysed following EGPA-SDS by Ponceau S staining to visualise MBP and MBP-CDK11p58 (left). The membrane was then probed by anti-V5 antibody to reveal the bound Plk4 recombinant protein. The input (1/25th) is also shown on the gel. Thus, Plk4 and CDK11p58 can bind directly to each other.