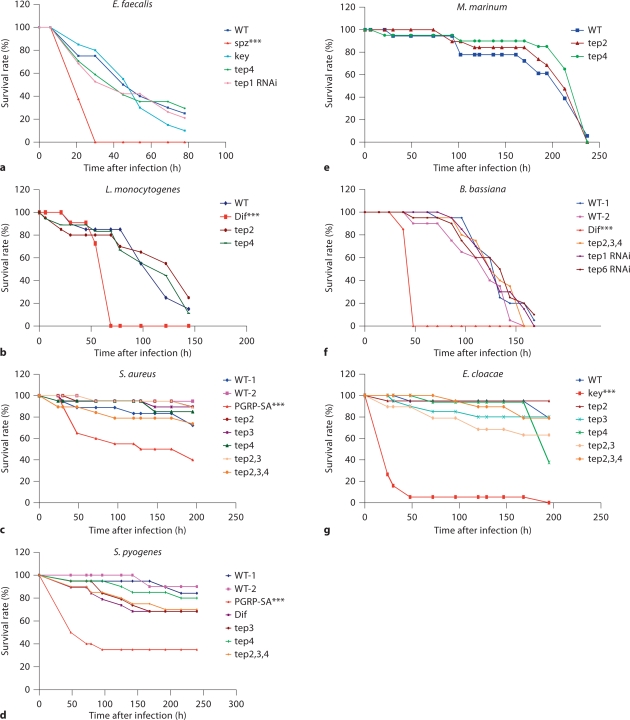
Fig. 6.
Tep mutants survive as wild-type (WT) flies to different types of infection. Survival experiments after distinct challenges in the septic injury model are presented and are representative of at least two independent experiments. The appropriate controls for the different microbes have been used: Gram-positive bacteria, fungi: mutants of the Toll pathway [Dif, spätzle (spz), PGRP-SA] and IMD pathway: kenny (key). None of the Tep mutants shows a reproducible susceptibility or resistance to infection phenotype, either in homozygous or hemizygous conditions. We used the logrank test to determine the significance between wild-type and mutant survival curves. ∗∗∗ p < 0.001 was the only constantly measured p value in several experiments.