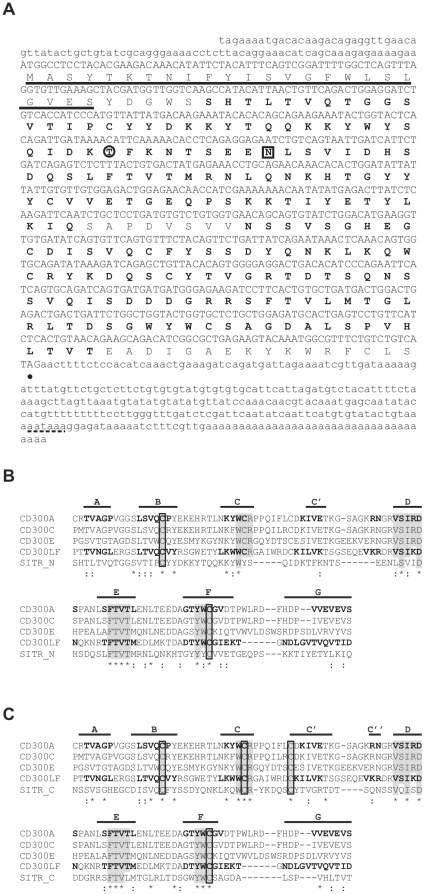
Figure 1. Carp Soluble Immune-Type Receptor (SITR) is a member of the Ig superfamily.
A. Nucleotide sequence of common carp SITR with open reading frame (upper case) and untranslated 5′ and 3′ regions (lower case). The predicted amino acid sequence is shown below the nucleotide sequence. The predicted signal peptide is underlined and the two Ig-like domains are marked in bold. The potential N-glycosylation site is boxed and the potential PKC interaction site is circled. Dot indicates the stop codon. A consensus polyadenylation signal (AATAAA) in the 3′-UTR is dashed. B. Alignment of the putative carp SITR N-proximal Ig-like domain (SITR_N, residues 30–123) with V-type Ig domains from human CD300 molecules. C. Alignment of the putative carp SITR C-proximal Ig-like domain (SITR_C, residues 132–224) with V-type Ig domains from human CD300 molecules. Asterisks indicate identity and colons denote similarity. Dashes indicate the introduced gaps to maximize the alignment. Residues characteristic of the V-type CD300 Ig-like fold and conserved between carp SITR (GenBank Accession Number: HM370297, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and human CD300A (GenBank acc no: NP_009192.2), CD300C (GenBank acc no: NP_006669.1), CD300E (GenBank acc no: NP_852114.1), CD300F (GenBank acc no: NP_620587.2) are grey shaded. Cysteines conserved between carp SITR and human CD300 molecules are boxed. Regions of β-strands, as defined by X-ray crystallography for CD300A (PDB acc no: 2Q87, http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do) and CD300LF (PDB acc no: 2NMS) are marked in bold. The positions of the predicted β-strands for carp SITR are indicated above the sequence.