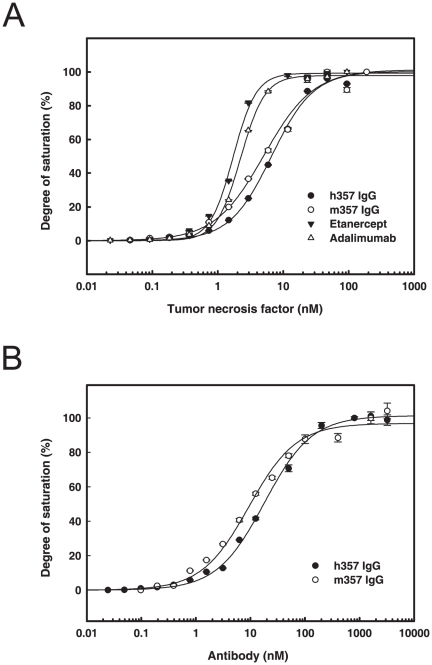
Figure 5. Binding affinities of h357 IgG to soluble and membrane form TNF-α.
(A) Binding affinities of different TNF-α anatagonists to soluble TNF-α. Microtiter plates with the anti-human IgG Fcγ fragment captured h357 (•), etanercept (▾) and adalimumab (△) and the anti-mouse IgG Fcγ fragment captured m357 (○) were incubated with various concentrations of soluble TNF-α for 1 hr at 37°C. After washing, the bound TNF-α was detected by a mouse monoclonal anti-TNF-α antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. Absorbance was read at 450 nm on a microplate reader. (B) The saturation binding curves of m357 and h357 IgGs to transmembrane TNF-α. Transmembrane TNF-α-transfected NS0 cells were incubated with serial log dilutions of m357 (○) or h357 (•) antibody for 1 hr at 4°C. Cell were washed and incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) for m357 and Alexa Fluor 647 goat anti-human IgG (H+L) for h357, respectively for 1 hr at 4°C. Cells were then washed and analyzed by FACSCalibur flow cytometer.