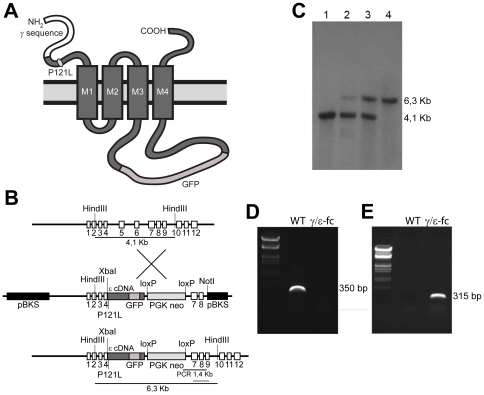
Figure 1. Generation and Structure of the γ/ε-fc Gene.
(A) Schematic representation of the recombinant AChRγ/ε-fc subunit, highlighting the location of the P121L mutation and the GFP insertion into the large cytoplasmic loop. (B) Diagram of the wild type γ subunit and targeting vector structure. Coding DNA sequences are represented by boxes. The ε cDNA (dark gray box) includes the P121L mutation and humanized EGFP sequence in the large cytoplasmic loop and is inserted into the genomic γ subunit DNA sequence at a XbaI restriction site in exon 4. The PGKneo cassette is spliced out of the primary mutated AChR ε subunit transcript. (C) Southern blot analysis of DNA from a wild type mouse (lane 1), positive ES cell clone (lane 2), heterozygous mouse (lane 3) and homozygous mouse (lane 4). The wild type γ subunit is represented by a 4.1 Kb fragment; the AChRγ/ε-fc subunit is represented by a 6.3 Kb fragment as indicated in B. (D, E) RT-PCR on RNA extracted from muscle of wild type (WT) or γ/ε-fc mice (γ/ε-fc). The γ subunit-specific primers yield a 350 bp fragment only for RNA from wild type muscles (D). The AChRγ/ε-fc subunit-specific primers yield a 315 bp DNA fragment for RNA from muscles of homozygous γ/ε-fc animals (E).