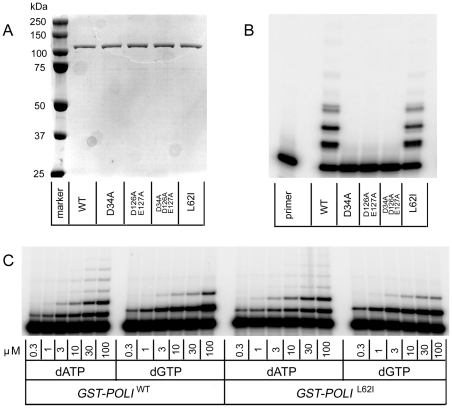
Figure 4. Activity of pure GST-tagged Pol ι variants.
A. Purification of GST-Pol ι and its variants by affinity chromatography: the photograph of a Coomassie brilliant blue stained gel is shown. Equal volumes (15 µl) of each fraction with wild-type GST-Pol ι, GST-Pol ιD34A, GST-Pol ιD126A/E127A, GST-Pol ιD34A/126A/E127A, and GST-Pol ιL62I eluted from the glutathione-sepharose column were analyzed on 8% SDS-PAGE. B. The comparative DNA-polymerase assay with purified GST-Pol ι and its variants. The ability of enzymes to extend a P32-labeled 17-mer primer annealed to template 1 was assayed in the presence of 100 µM of all four dNTPs and 0.15 mM Mn2+ ions, at 37°C for 5 min. C. Kinetic analysis of dATP and dGTP incorporation by purified wild-type GST–Pol ι and GST–Pol ι L62I variant. Primer extension reaction was carried out in the presence of 0.15 mM Mn2+ divalent metal ions and 1 nM of GST-Pol ι or its catalytically compromised variant at 37°C for 2.5 min. To quantify the incorporation of dATP and dGTP opposite template T we varied each dNTP concentration from 0.3 to 100 µM. Kinetic parameters determined from these experiments were: Wild-type: dATP: Km = 3.5±1 µM, Vmax = 9.8±0.8 (% incorporation/min), dGTP: Km = 0.57±0.08 µM, Vmax = 14.9±0.3 (% incorporation/min), finc for dGTP = 5.3; and L62I: dATP: Km = 4.0<0.9 µM, Vmax = 11.4±0.8 (% incorporation/min), dGTP: Km = 0.54±0.09 µM, Vmax = 17.2±0.3 (% incorporation/min), finc for dGTP = 6.1.