Figure 2. Stability of FN and susceptibility to cleavage by MMP-2 as a function of purification and protease inhibitors.
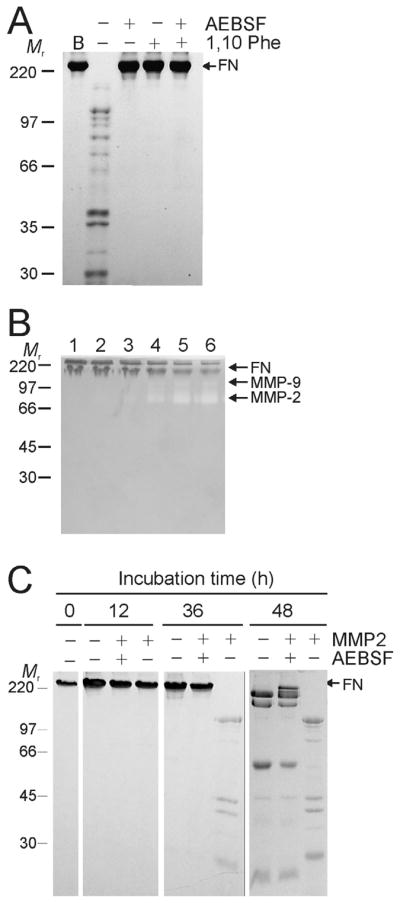
Panel A. The stability of FN in 50 mM Tris, 0.15 M NaCl, pH7.4 following purification from human plasma by gelatin-Sepharose affinity chromatography (B)(See also Fig. 1) was analyzed in the presence or absence of 0.5 mM 4-(2-aminoethyl)-benzenesulfonyl fluoride (AEBSF) serine protease inhibitor and 1.5 mM 1,10 phenanthroline (1,10 Phe) MMP inhibitor. FN cleavage was monitored by 7.5% SDS-PAGE for 48 h at 22°C. FN demonstrated significant fragmentation in the absence of the inhibitors, whereas both inhibitors blocked hydrolysis. Panel B. To eliminate effects of co-purified MMP-2 and -9, urea-eluted FN from the gelatin-Sepharose affinity column was exchanged into 50 mM sodium-phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.0 and further purified by gel filtration (HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 200). Eluted fractions in which no gelatinolytic activities were detected by gelatin-zymography (lanes 1, 2) were separated from those that contained MMP-2 and -9 (lanes 3–6), pooled, and used for subsequent analyses. Panel C. The capacity of exogenous recombinant MMP-2 to cleave FN was tested in preparations void of plasma-derived MMPs in the presence or absence of AEBSF over 48 h at 22 °C. Analysis of reactions by 10% SDS-PAGE gels showed significantly greater cleavage of FN by MMP-2 in the absence of AEBSF pointing to synergic actions of MMP-2 and serine protease-like proteolytic activities. Positions of FN and masses (kDa) of protein markers (Mr) are indicated.
