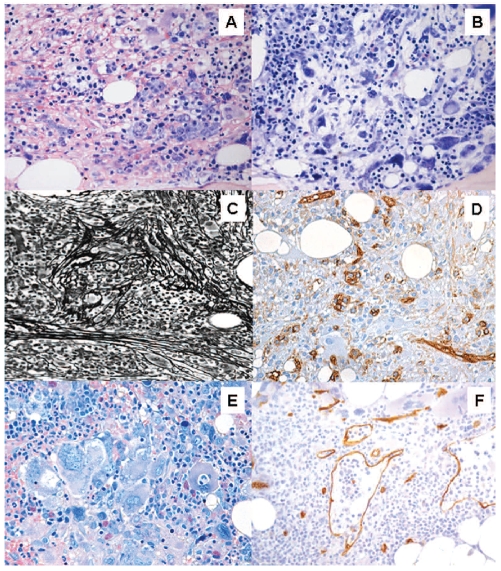
Figure 1.
Typical histological findings in myelodysplastic syndrome with bone marrow fibrosis (MDS-F). These include: (A) increased bone marrow cellularity with erythroid hyperplasia, (B) dysplastic megakaryocytes (such as hypolobulated megakaryocytes) with uncommon sizeable clusters, (C) bone marrow fibrosis (Gomori’s silver impregnation) and (D) the presence of clusters of CD34+ cells. A critical issue in clinical practice is the differential diagnosis from primary myelofibrosis. High bone marrow cellularity, increased bone marrow CD34+ cells and multilineage dysplasia are closely associated with MDS-F. Distinctive features of primary myelofibrosis are (E) megakaryocytic hyperplasia with megakaryocyte clusters and cloud-like or balloon-shaped megakaryocytic nuclei, and (F) dilation of marrow sinuses with intrasinusoidal hematopoiesis (Courtesy of Emanuela Boveri).