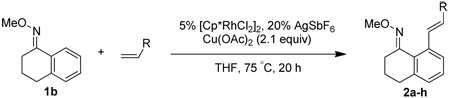
Table 2.
Alkene Scopea
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| entry | alkene | product | yieldb |
| 1 | 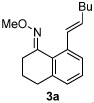 |
75% | |
| 2 |  |
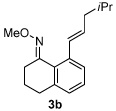 |
84% |
| 3 | 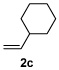 |
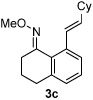 |
53% |
| 4 | 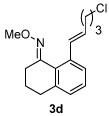 |
85% | |
| 5 | 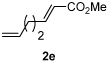 |
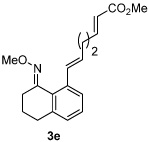 |
80% |
| 6 | 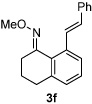 |
98% | |
| 7 | 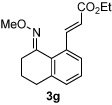 |
81% | |
| 8 | 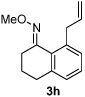 |
46% | |
All reactions were performed by heating the oxime (1 equiv), alkene (3 equiv), [Cp*RhCl2]2 (5 mol %), AgSbF6 (20 mol %), Cu(OAc)2 (2.1 equiv), and THF (0.1 M) in a sealed vial for 20 h at 75 °C.
Isolated yields after purification by chromatography are reported.
