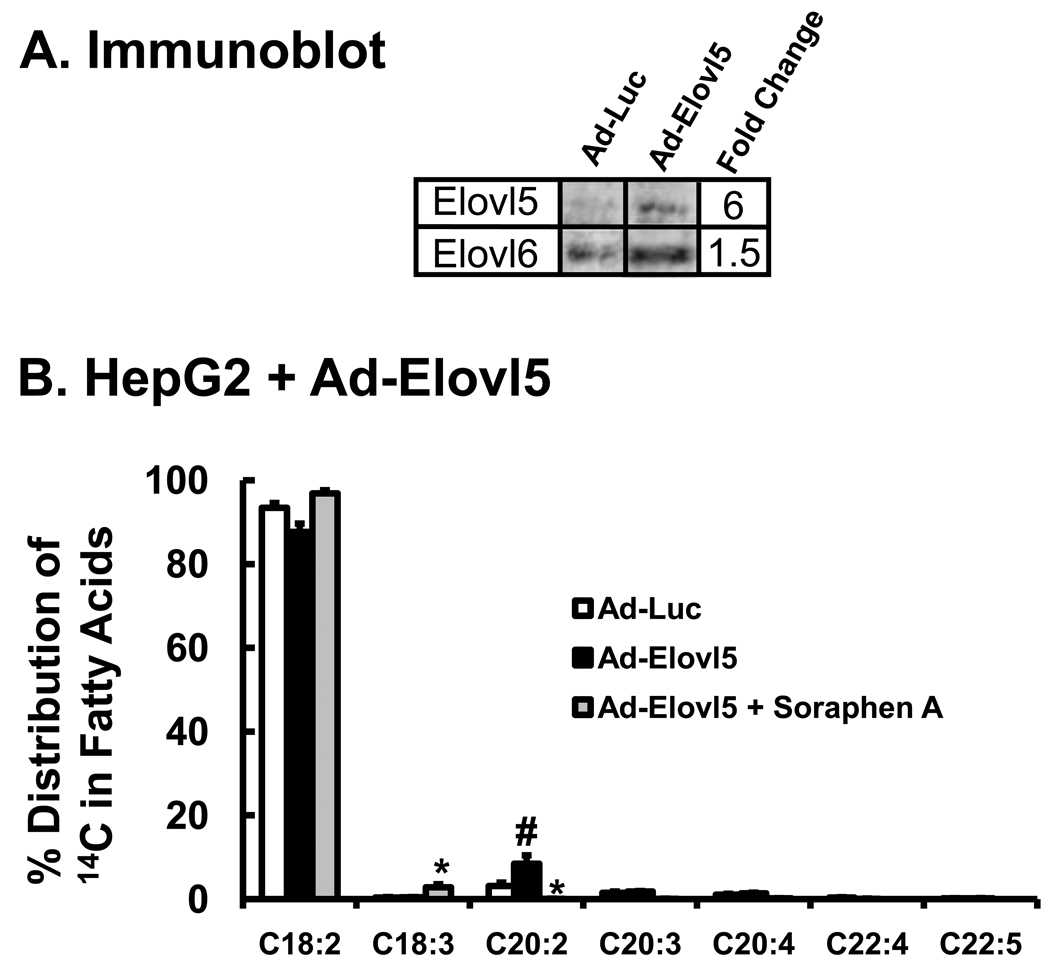
Figure 5. Effect of elevated Elovl5 expression on soraphen A regulation of 18:2,n-6 metabolism in HepG2 cells.
A: Immunoblot analysis for Elovl5. HepG2 cells were infected with Ad-Luc (control virus) or Ad-Elovl5 at 20 PFU/cells 48 hrs prior to treatment with [1-14C]-18:2, n-6 (Methods). The immunoblot represents the level of Elovl5 protein abundance in HepG2 following infection with Ad-Luc or Ad-Elovl5 prior to fatty acid treatment. Ad-Luc has no effect on Elovl5 protein abundance; Ad-Elovl5 infection increases Elovl5 protein 5-fold, a value consistent with physiological changes seen in vivo [24, 25]. B: Forty-eight hours after Ad-Luc or Ad-Elovl5 adenoviral infection, cells were treated with DMSO, soraphen A and [1-14C]-18:2,n-6 (50 µM) as described above. Six hours after treatment cells were harvested for extraction and saponification. 14C-fatty acids were fractionated as described (Methods). Treatments: Ad-Luc + DMSO (white bars); Ad-Elovl5 + DMSO (black bars); Ad-Elovl5 + soraphen A (gray bars). Results are expressed as % Distribution of 14C Fatty Acids; mean ± SD, n=3; *, p≤0.05 DMSO versus soraphen A; #, p≤0.05 Ad-Luc versus Ad-Elovl5; t-test.