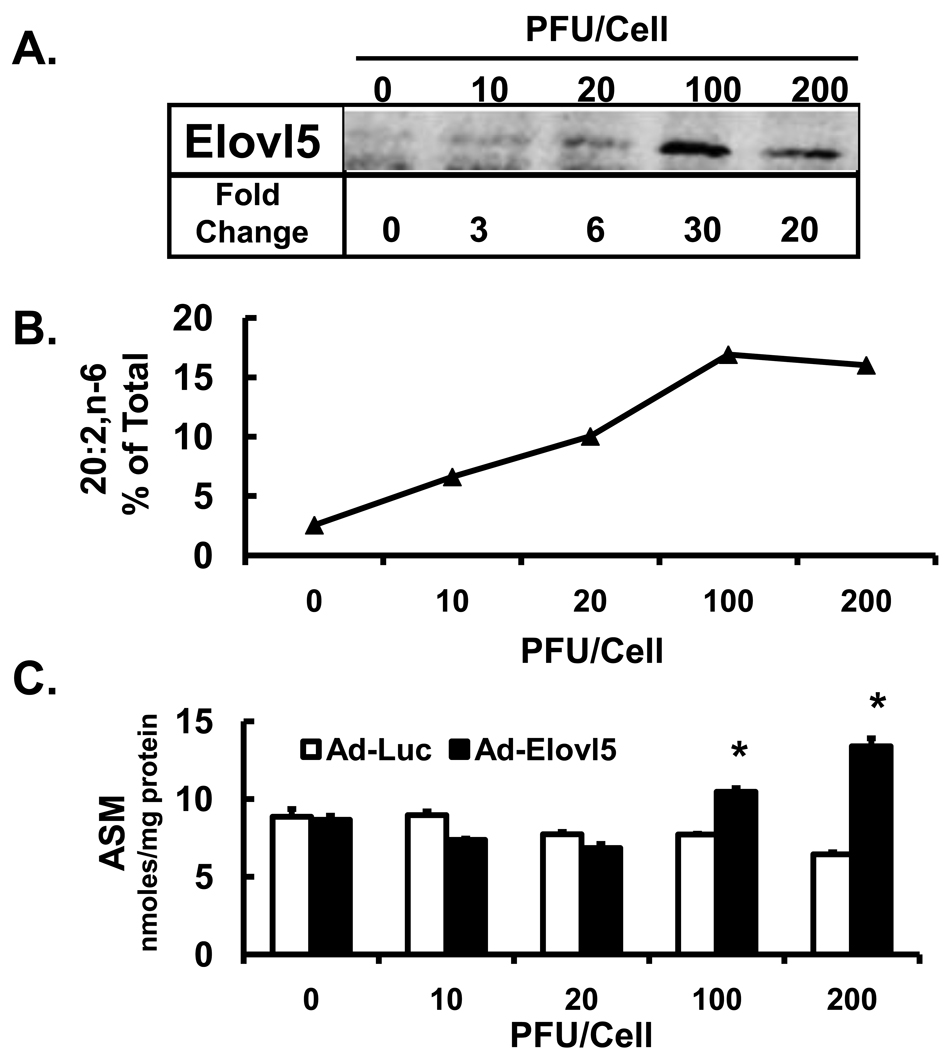
Figure 8. High levels of Elovl5 expression increases fatty acid oxidation of 18:2,n-6.
HepG2 cells were infected with Ad-Luc or Ad-Elovl5 at 10–200 PFU/cell 48 hrs before fatty acid treatment. [Panel A]: Levels of Elovl5 were quantified by immunoblot (Methods). [Panel B]: Cells were treated with 50 µM [1-14C]-linoleate for 6 hrs and harvested for total lipid extraction and saponification for RP-HPLC fractionation and quantitation of 14C-20:2,n-6. Results are presented as 20:2,n-6, % of Total 14C-fatty acid recovered by RP-HPLC. [Panel C]: Media was harvested for analysis of 14C-linoleic acid oxidation products, i.e., acid soluble material (ASM, nmoles/mg protein). Results are the mean ± range of 2 separate studies. *. P≤0.05 versus DMSO, t-test.