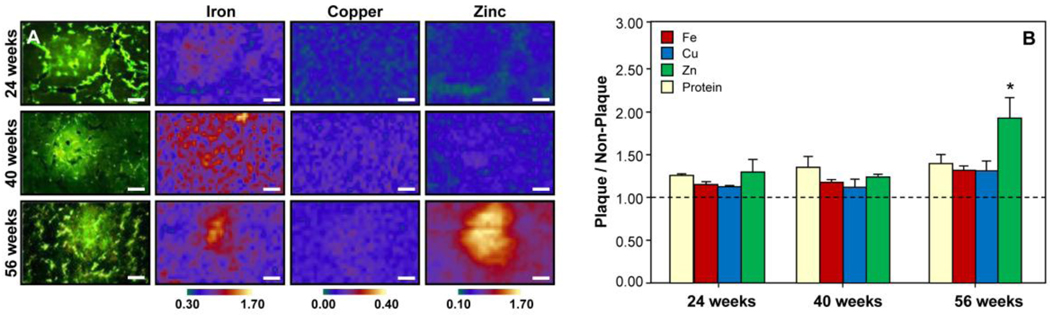
Figure 4.
Metal ion content in amyloid plaques at 24, 40, and 56 weeks. (A) Thioflavin S-stained PSAPP mouse brain tissue and corresponding XFM images of Fe, Cu, and Zn in the plaques and surrounding non-plaque tissue. All scale bars are 25 µm. (B) Ratio of Fe, Cu, Zn, and protein content in the plaque vs. non-plaque tissue. At 56 weeks, the plaques showed elevated Fe, Cu, and Zn content. However, the protein density in the plaques also increased by 11% from 24 to 56 weeks. Thus, when normalized to protein density, Cu and Fe were actually lower in the plaques than the surrounding tissue and only the Zn content was significantly elevated by 38% in the plaques (p < 0.05). [* indicates significantly different from 40 week-old mice (p < 0.05).]