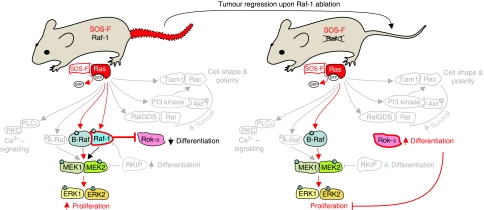
Figure 2.
Ras-driven tumours are addicted to Raf-1. Ras-driven tumours, induced by the keratinocyte-restricted expression of membrane-tethered SOS (SOS-F transgenic mice; red, irregularly shaped tail) regress upon keratinocyte-specific ablation of Raf-1, indicating an essential role of this molecule in tumour maintenance. Downstream of Ras, Raf-1 is involved in at least two pathways: the canonical Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, where Raf-1 acts as an activator, likely in the context of a Ras-induced heterodimer with B-Raf; and the Rok-α pathway, where Raf-1 acts as an inhibitor via direct protein–protein interaction (left panel). Upon Raf-1 ablation (right panel; Raf-1 crossed out), ERK phosphorylation continues undisturbed, likely sustained by B-Raf; Rok-α, however, is strongly activated, leading to increased differentiation, and to tumour regression.