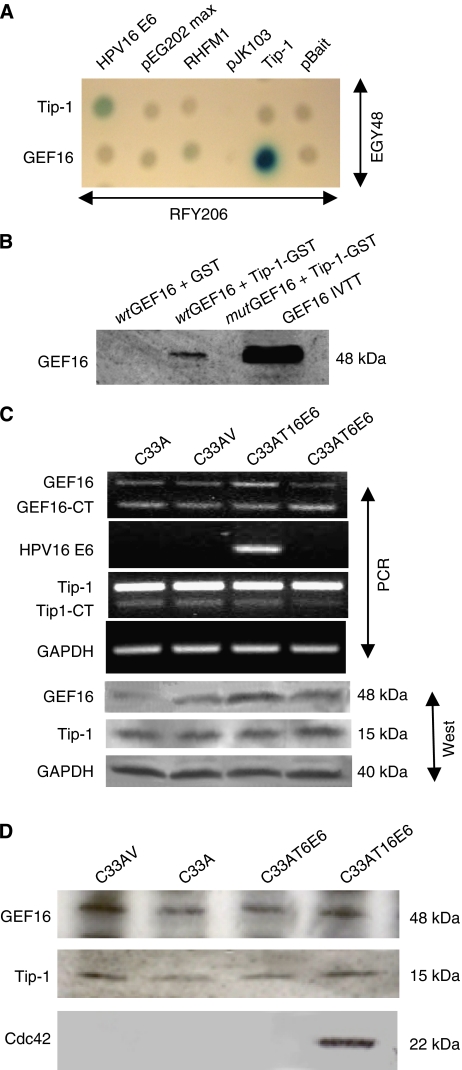
Figure 1.
Interactions, regulation and stability of GEF16. (A) Yeast mating assay confirming that Tip-1 binds to short carboxyl terminal GEF16 fragments isolated from the primary Tip-1 yeast two-hybrid screen. (B) Glutathione transferase pull-down of Tip-1 with IVTT full-length wild-type and mutant GEF16 (wtGEF16/mutGEF16). The wtGEF16 contains the PDZ-binding domain ETDV, whereas mutGEF16 has the TDV residues deleted. Tip-1-GST fusion protein and GST control protein were bound to glutathione-sepharose beads. These were mixed with equal amounts of the IVTT wtGEF16 or mutGEF16 proteins, and then washed with binding buffer. Bound proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and visualised by western immunoblotting with anti-GEF16. The GST-Tip-1 protein bound to the wtGEF16, but did not bind to the mutant form, whereas the GST control did not bind either product. (C) Competitive template RT–PCR and western blot analysis of GEF16 and Tip-1 expression in mRNAs and proteins extracted from C33A, C33AV, C33AT16 E6 and C33AT6 E6 cells. mRNA's were reverse transcribed and the resulting cDNAs PCR amplified using primers specific for GAPDH, HPV16 E6, GEF16 and Tip-1 by competitive template PCR. Total proteins were extracted from the same cells, separated by SDS–PAGE, electroblotted and immunoprobed with anti-GEF16 and anti-Tip-1. Anti-GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) Immunoprecipitation with anti-GEF16 from lysates of C33AV, C33AT16 E6 and C33AT6 E6 cells treated with 10 μM of the selective proteasome inhibitor MG132 for 4 h. When immunoprobed with Tip-1 and Cdc42, it can be seen that Tip-1 is associated with GEF16 in both the presence and absence of T16 E6. Cdc42 was detected in association with the GEF16 complex in the presence of HPV type 16 E6, but not in type 6 or vector and parent control cells. (GEF16 has a putative Cdc42 binding site at amino acids 385–391 (QRTLQKL)).