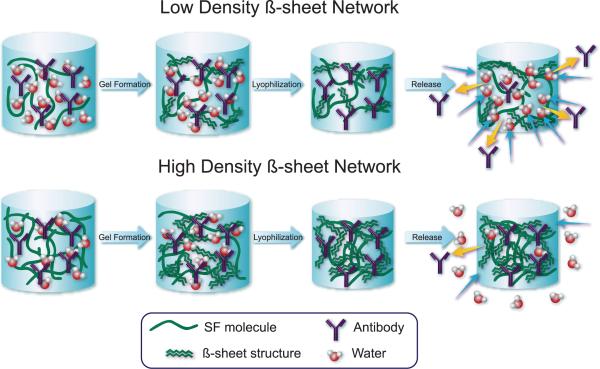
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of water uptake and antibody release behavior for low (~20 mg (cm3)−1) and high (>35 mg (cm3)−1 β-sheet density silk lyogels. Removal of water by lyophilization leads to increased silk-antibody interactions. Interactions are more numerous in the high density β-sheet samples, trapping a larger fraction of antibody. Increased hydrophobicity of the high density β-sheets also retards water uptake, decreasing swelling and antibody release.