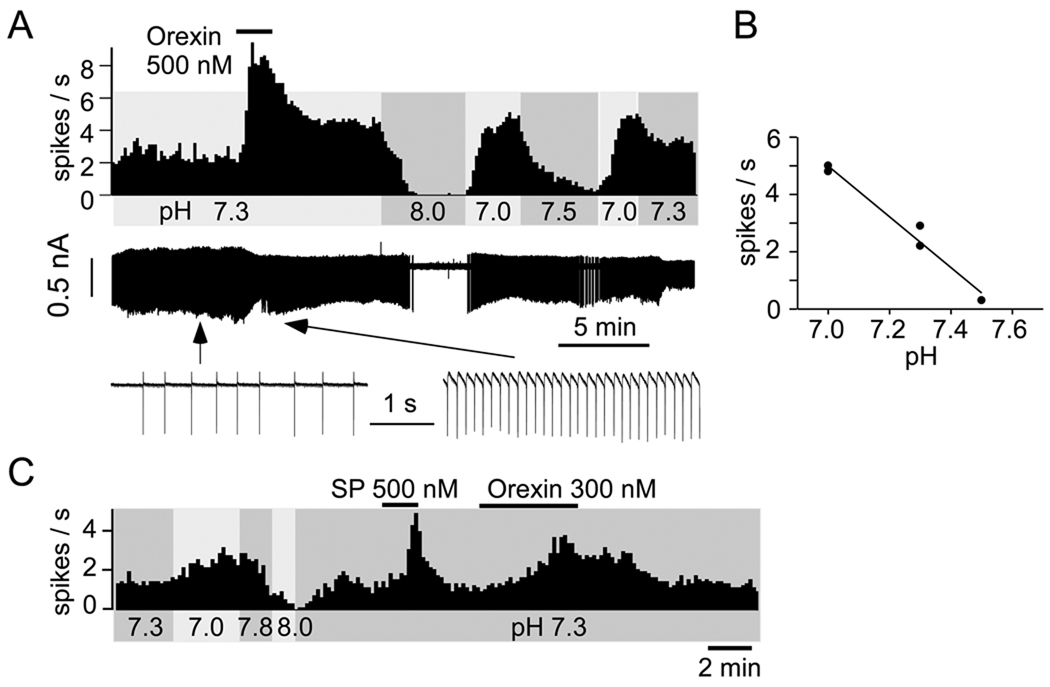
Figure 2. Effect of pH and orexin on RTN neurons: representative examples.
A. Top trace: discharge rate of one RTN neuron (integrated rate histogram, 10 s bins, JX99 mouse). Middle trace: raw recording of action currents recorded in loose-patch mode. Lower trace: action currents shown at higher resolution before and during application of orexin. B: steady-state relationship between discharge rate and pH in the absence of orexin for the neuron shown in A. C. discharge of one RTN neuron in a B/G Phox2b-eGFP mouse (integrated rate histogram, 10 s bins). Substance P (SP; 500 nM) was also applied to this neuron, producing the expected vigorous activation (Mulkey et al., 2007).