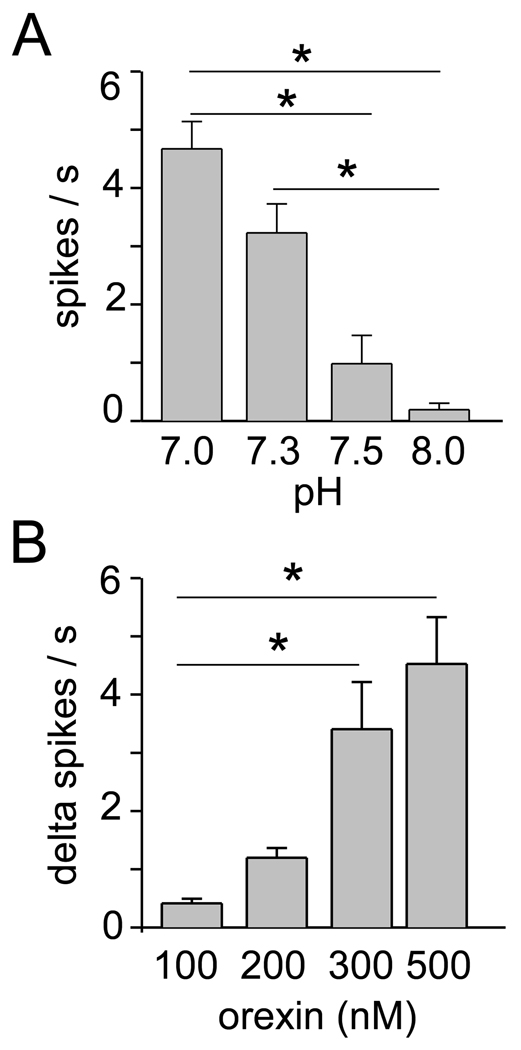
Figure 3. Effect of pH and orexin on RTN neurons: group data.
A. Effect of bath pH on the steady-state discharge of 14 RTN neurons. There was a highly significant effect of pH on the discharge rate (P<0.001 by Kruskall-Wallis ANOVA on ranks). B. Increase in discharge rate elicited by four concentrations of orexin in the same 14 neurons recorded at pH 7.3 (up to 2 concentrations tested per neuron, 4 determinations for the 100, 300, and 500nM levels, 6 for the 200 nM concentration). There was a highly significant dose-effect relationship (P=0.002 by Kruskall-Wallis ANOVA on ranks). Asterisks denote statistically significant pair-wise comparisons. The pairs are identified by the end of the horizontal lines.