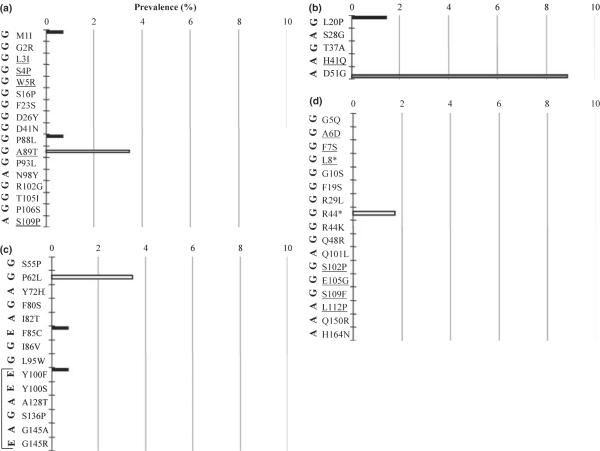
Fig. 3.
Prevalence of (a) PreS1, (b) PreS2, (c) S and (d) polymerase spacer [Pol(PS)] mutations identified in Occult hepatitis B virus infections in genotype A, E and G reference sequences. None of the identified polymerase reverse transcriptase mutations [Pol(S)] were found in any of the additional reference sequences. (*) Indicates a stop codon. Black bars indicate prevalence in genotype A sequences, white bars indicate prevalence in genotype E sequences, and grey bars indicate prevalence in genotype G sequences. The original genotype in which each mutation was identified is indicated on the left in bold. Underlined mutations could not be analysed in all genotypes because of genotype-specific sequence differences. Bracket in (c) indicates mutations present in the antigenic determinant of hepatitis B surface antigen (amino acids 100–165).