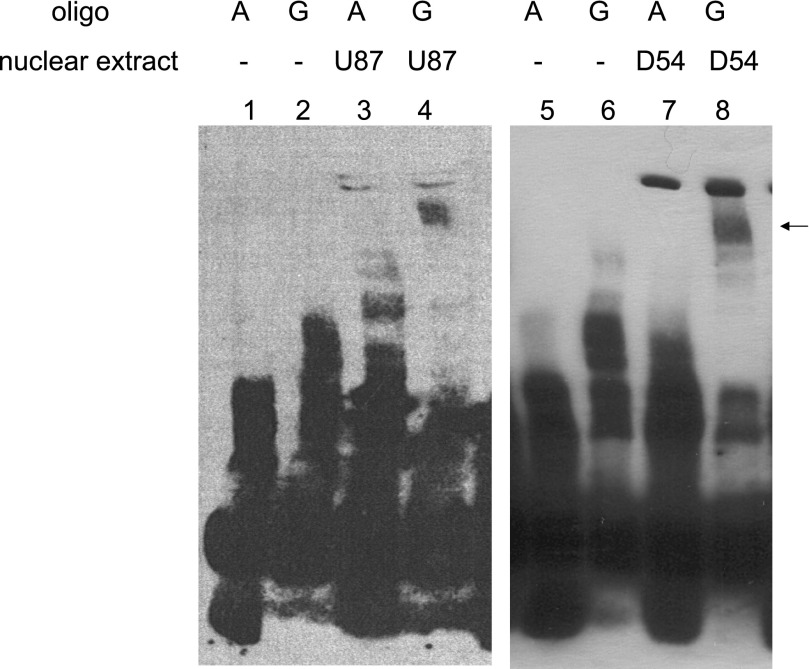
Fig. 2.
Allelic polymorphisms of rs3734967 residing in the promoter of HTR5A present distinct binding patterns with nuclear proteins from brain cells. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed in two different human glioma cell lines, U-87 (lanes 3 and 4) and D-54 (lanes 7 and 8). Oligos carrying rs3734967 and its surrounding sequence were assayed for binding capabilities with proteins from the two types of nuclear extracts. A pattern is consistently observed in both cell lines showing that the G allele (lanes 4 and 8) binds unidentified protein factors, causing a mobility shift in the electrophoresis. This pattern does not appear for the A allele (lanes 3 and 7), nor for the A or the G allele when no nuclear protein is applied (lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6). The arrow points at mobility shift of oligonucleotides with the G allele caused by differential protein binding. Results are representative of at least 4 separate experiments.