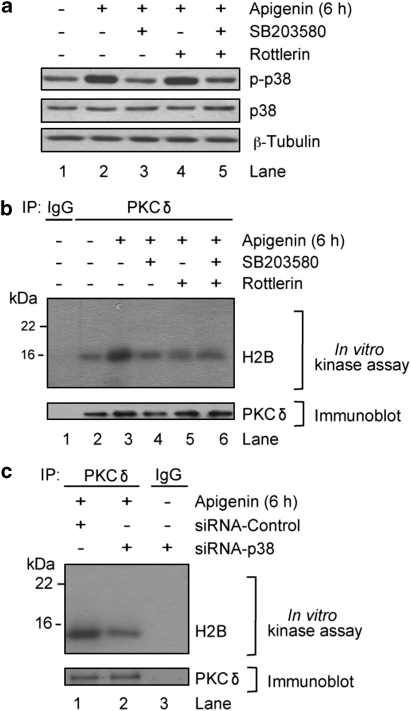
Figure 6.
p38-MAPK modulates apigenin-induced PKCδ activity. THP-1 cells treated with 50 μM apigenin for 6 h alone or following 1 h pretreatment with 10 μM SB203580, a p38 inhibitor, 15 μM rottlerin, a PKCδ inhibitor, or both, and lanes marked with (−), denote addition of diluent, were (a) immunobloted with anti-phospho-p38, anti-total-p38, and anti-β-Tubulin antibodies. (b) Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKCδ antibodies or an isotype control (IgG), followed by in vitro kinase assay in the presence of (γ-32P)ATP and H2B as a substrate. Kinase products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Phospholabeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. The same membrane was immunoblotted with anti-PKCδ antibodies as loading control. (c) Lysates from THP-1 cells transfected with siRNA-Control or siRNA-p38 were treated for 6 h with 50 μM apigenin and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKCδ antibodies or an isotype control (IgG), followed by in vitro kinase assay in the presence of (γ-32P)ATP and H2B as a substrate. Kinase products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Phospholabeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. The same membrane was immunoblotted with anti-PKCδ antibodies as loading control. Results are a representative of three independent experiments