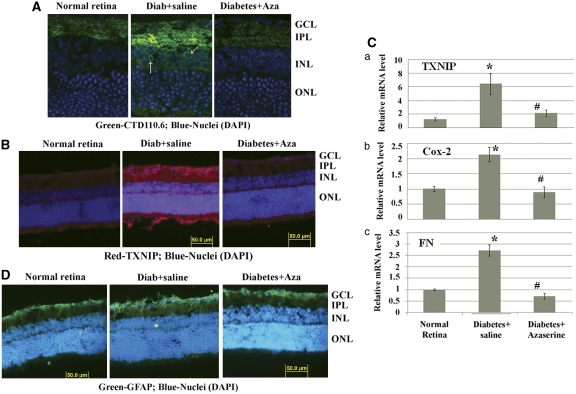
Figure 3.
Blockade of the HBP by azaserine prevents TXNIP expression, inflammation and gliosis in the diabetic retina. Intravitreal injection of azaserine, an inhibitor of the HBP, in the right eye of diabetic rats reduces protein O-GlcNAcylation (A), which corresponds to a decrease in TXNIP expression in the same retina (B). A representative of n=3 is shown here. The left eye of the same diabetic rats was injected with saline and used as the corresponding diabetic control retina. (C) RT-qPCR analysis for TXNIP, Cox-2 and FN mRNAs shows their elevated levels that are blunted by azaserine. *Significant change (P<0.05, n=6) for diabetic retina (left eye injected with saline) versus normal retina; #significant decrease (P<0.05, n=6) in gene expression after azaserine treatment (right eye) when compared with saline-treated left eyes of the same animal. (D). Diabetes induces glial cell reactivity in the retina as demonstrated by increased GFAP expression in intermediate filaments, which extend from epiretinal membrane to photoreceptor ONL. Azaserine prevents GFAP expression in the diabetic retina, which is more or less comparable to GFAP levels in normal rat retina. A representative of n=3 is shown here