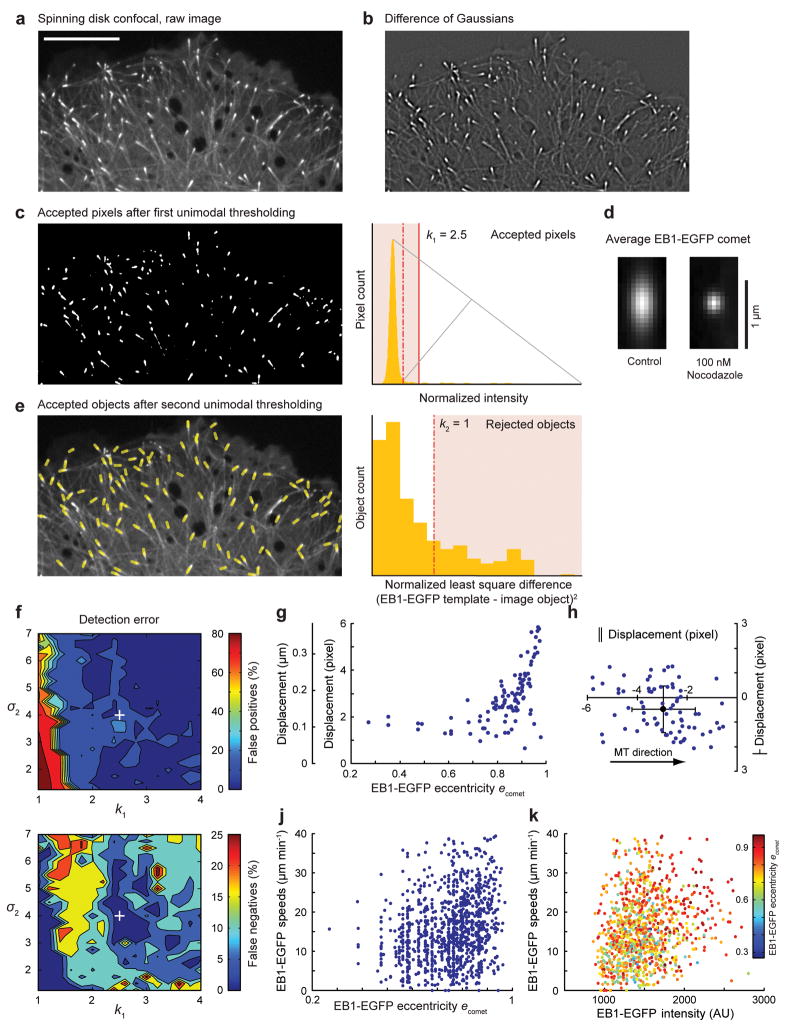
Figure 1. EB1-EGFP Comet Detection.
(a) Spinning disk confocal image of a cell expressing EB1-EGFP. (b) Difference of two Gaussian (DoG) transformation applied to image in a). (c) Accepted pixels (white) after unimodal intensity thresholding; The plot (right) shows the histogram of normalized DoG intensities; grey lines illustrate construction of the unimodal threshold; dashed red line, automatic threshold; solid red line, threshold modified for confocal images. (d) Average EB1-EGFP comets in a control and nocodazole-treated cell. (e) Positions and orientation of accepted comets (yellow lines, overlaid on raw image) based on automatic thresholding. The plot (right) shows the histogram of the normalized least squares difference between individual comet images and the average of all comets in this frame. (f) Contour plots show detection error (top, false positives; bottom, false negatives) as a function of σ2 and k1. The white cross indicates the detection parameters used in (a) ([σ1, σ2, k1, k2] = [1, 4, 2.5, 1]. (g) Displacement of computer-detected EB1-EGFP comet position relative to hand-detected microtubule end as a function of comet eccentricity (g) and as a function of orientation relative to the microtubule direction (h). Only comets with an eccentricity e > 0.8 (~70% of the total comet population in this image) were used in (h). Solid circle, mean displacement; error bars, s.d. (n = 95) (j, k) EB1-EGFP comet eccentricity (j) and intensity (k) are plotted versus comet speed.