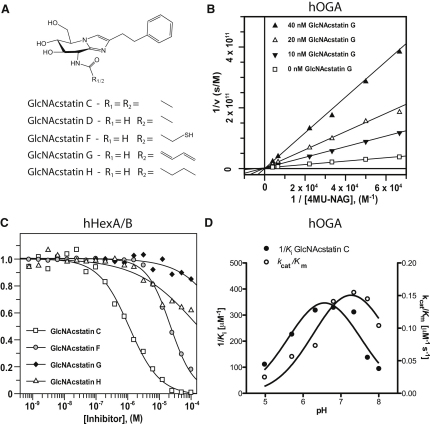
Figure 1.
GlcNAcstatins and Their Inhibitory Activities
(A) Chemical structures of GlcNAcstatins C, D, and F–H.
(B) Lineweaver-Burk analysis of hOGA steady-state kinetics measured in the presence of 0–40 nM GlcNAcstatin G at pH 7.3. Data were fitted using the standard equation for competitive inhibition in the GraFit program (Leatherbarrow, 2001), yielding a Ki of 4.1 nM (Table 1).
(C) Dose-response curve of hHexA/B inhibition GlcNAcstatins C and F–H. Data were fitted using the standard IC50 equation in the GraFit program (Leatherbarrow, 2001).
(D) Characterization of pH optimum of hOGA catalytic activity (open circles) and GlcNAcstatin C inhibition (black dots). The catalytic activity was measured using a McIlvaine buffer system over a 4.9–8.1 pH range. Data for 1/Ki and kcat/Km were plotted versus the pH and fitted by nonlinear regression to the bell-shaped double pKa equation in the program GraphPad Prism. The pH optimum for hOGA hydrolytic activity is pH 7.3 (right y-axis), and the pH optimum GlcNAcstatin C inhibition is at pH 6.6 (left y-axis).