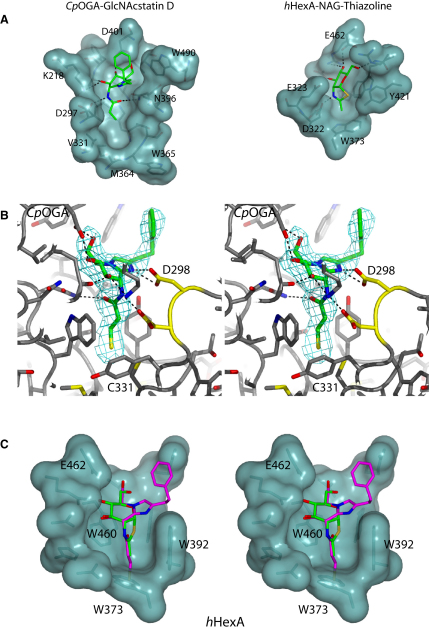
Figure 2.
Binding of GlcNAcstatins to CpOGA
(A) Comparison of the active-site architecture of OGA enzymes and hexosaminidases. The active site of CpOGA in complex with GlcNAcstatin D (PDB entry 2WB5) (Dorfmueller et al. [2009]) is shown in a semitransparent surface representation. GlcNAcstatin D is shown in sticks with green carbon atoms. hHexA in complex with NAG-thiazoline (PDB entry 2GK1) (Lemieux et al. [2006]) is shown with NAG-thiazoline in sticks with green carbon atoms. The residues blocking the active site from this side view (Tyr335 in CpOGA and Trp392 in hHexA) have been removed in these images for clarity. Hydrogen bonds between the ligands and active site residues are indicated by black dashed lines.
(B) Stereo figure of the crystal structure of GlcNAcstatin F (sticks with green carbon atoms) in complex with V331C-CpOGA. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by black dashed lines. An unbiased |Fo |− |Fc |, φcalc electron density map calculated without the model having seen the inhibitor in refinement is shown at 2.75 σ.
(C) Stereo figure of a superimposition of GlcNAcstatin F onto the hHexA-thiazoline complex. Semitransparent surface representation of hHexA in complex with NAG-thiazoline (green carbon atoms) (PDB entry: 2GK1) (Lemieux et al. [2006]). GlcNAcstatin F (magenta carbon atoms) is superimposed onto NAG-thiazoline.