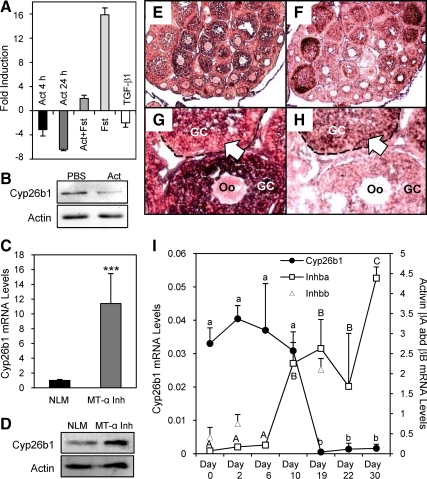
Figure 4.
Activin regulation of Cyp26b1 gene expression and the inverse correlation of Cyp26b1 and activin βA mRNA expression. A, Effects of activin A (Act), activin A+follistatin (Act+Fst), follistatin (Fst) alone, and TGF-β1 on Cyp26b1 mRNA levels in primary cultured granulosa cells (P < 0.05 for all, n = 3). B, Effect of activin A (Act) on Cyp26b1 protein levels. Actin was detected as a loading control. C, Comparison of Cyp26b1 mRNA levels in MT-α inhibin transgenic (MT-α Inh) mouse ovaries with those in the NLM ovaries. ***, P < 0.0001 (n = 7). D, Western blot pictures showing Cyp26b1 protein levels in NLM and MT-α Inh mouse ovaries. Actin was detected as a loading control. E–H, In situ hybridization of Cyp26b1 (E and G) and activin-βA (F and H) in postnatal d 20 ovaries. E and F show lower magnification; G and H show higher magnification. Complementary expression patterns of Cyp26b1 and activin-βA mRNA within one follicle is indicated by open arrows. GC, Granulosa cells. Oo, oocytes. I, Comparison of mRNA levels of Cyp26b1, activin-βA (Inhba), and activin-βB (Inhbb) in developing ovaries as measured by real-time PCR. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences, according to ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test (lowercase letters for Cyp26b1; uppercase letters for activin βA). P < 0.05 (n = 3–5).