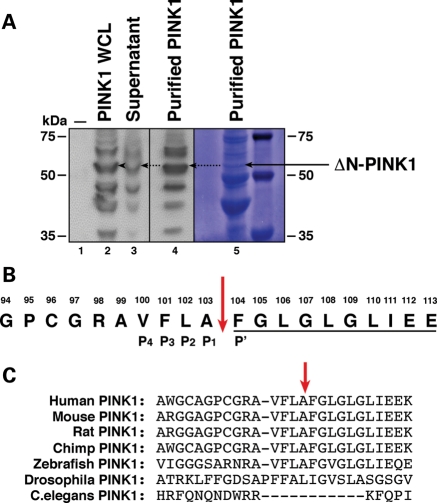
Figure 1.
Isolation of ΔN-PINK1 and identification of the cleavage site. (A) WB analysis of vector control-transfected HEK293T cells (lane 1), PINK1-3xHA expression in whole-cell lysate samples before purification with anti-HA beads (lane 2), the presence of residual unbound PINK1-3xHA in supernatant post-purification (lane 3) and enrichment of the ΔN-PINK1 protein in the purified sample (lane 4). WBs were performed using an anti-HA antibody. Lane 5 displays the presence of the ΔN-PINK1 protein assessed by Coomassie staining. This membrane was then sent for N-terminal Edman degradation sequencing analysis. (B) N-terminal Edman sequencing result. The 10 amino acids underlined display the amino acid read obtained during the analysis. The sequence of PINK1 spanning amino acids 94–112 is shown with the cleavage site highlighted by a red arrow. The P4–P1 and P′ sites of the PINK1 cleavage site are also indicated. (C) Sequence alignment of the PINK1 protein surrounding the cleavage site showing conservation between mammalian species. Alignment was performed in Clustal X.