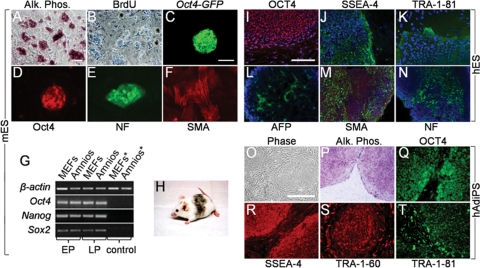
Figure 6.
Mitotically inactivated amniocytes function as feeder layers for mES, hES and hAdiPS cells. (A and B) Mitomycin C-treated mouse amniocytes function as feeder layer for R1 mES cells. After 10 passages (30 days) in culture, mES cell colonies demonstrate AP activity and BrdU labeling. (C and D) Oct4-GFP reporter fluorescence and Oct4 immunostaining of mES colonies cultured for 30 days on amniocyte feeders. (E and F) NF and SMA immunostaining after 7 and 14 days of in vitro differentiation, respectively. (G) RT–PCR analysis of Oct4, Nanog and Sox2 expression in early (E, <3) and late (L, >10) passage mES cells maintained on MEFs or mouse amniocytes. Controls (*) are feeders without mES cells. (H) Germline competent chimera from blastocyst injection of mES cells maintained for 50 days (15 passages) on mouse amniocyte feeder layer. (I–K) OCT4, SSEA-4 and TRA-1-81H1 immunoreactivity in hES cells cultured for 21 days (six passages) on γ-irradiated human amniocytes. (L–N) AFP, SMA and NF immunostaining after EB differentiation of H1 hES cells cultured on γ-irradiated human amniocytes. (O–T) γ-irradiated human amniocyte feeder layers support growth and self-renewal of hAdiPS cells derived from the same amniocytes. After 21 days (five passages) in culture, hAdiPS cell colonies demonstrate AP activity and OCT4, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60 and TRA-1-81 expression by immunocytochemistry. mES and hES cells, mouse and human embryonic stem cells; AP or Alk. Phos., alkaline phosphatase; BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; Amnios, mouse amniocytes; MEFs, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; EP, early passage; LP, late passage; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; SMA, smooth muscle actin; NF, neurofilament. Scale bars: 100 μm.