Fig. 1.
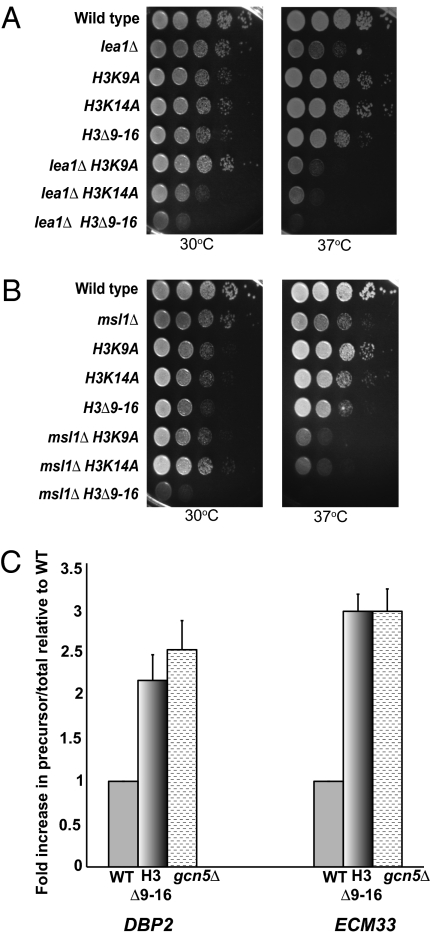
Mutation of histone H3 residues combined with deletion of either MSL1 or LEA1 leads to severe synthetic growth defects. (A) Growth analysis of the double-mutant lea1Δ and histone H3 point mutants or truncation. Cells were grown at 30 °C in YPD medium until the desired OD600 was obtained. Cells were spotted onto YPD plates as a 10-fold serial dilution and grown at 30 °C or 37 °C for 2 d. (B) Dilution series of the double mutant msl1Δ and histone H3 point mutants or truncation. Cells were treated as described in A. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR of DBP2 and ECM33 in the histone H3 truncation mutant histone H3Δ9–16 or gcn5Δ vs. wild-type. Data are represented as a fold-increase in the ratio of precursor (unspliced)/total DBP2 or ECM33 message relative to wild-type. Graph represents three independent experiments and error bars represent SEM.