Table 1. The six ligands of FKBP sorted according to binding affinity.
| Compound | Unbindinga events | Rebindingb events | Binding affinity (LIE model)c | Unbindingd | Experimentale value of K (mM)
(mM) |
||
| vdWaals | electr. | Total | time | ||||
| (kcal/mol) | (ns) | ||||||
| DMSO | 49 | 5 |
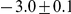
|
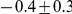
|
-3.4 |
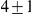
|
20.0 |
| PENT | 34 | 10 |
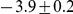
|
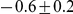
|
-4.5 |
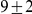
|
2.0 |
| BUT | 40 | 8 |
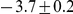
|
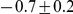
|
-4.4 |
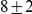
|
0.5 |
| DAP | 45 | 12 |
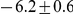
|
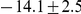
|
-20.3 |
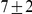
|
0.5 |
| DSS | 29 | 9 |
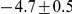
|
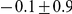
|
-4.8 |
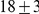
|
0.25 |
| THI | 32 | 10 |
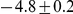
|
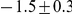
|
-6.3 |
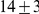
|
0.2 |
The six ligands are: BUT, 4-hydroxy-2-butanone; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; DAP, 5-diethylamino-2-pentanone; DSS, methyl sulphinyl-methyl sulphoxide; PENT, 5-hydroxy-2-pentanone; THI, tetrahydrothiophene 1-oxide.
An unbinding event is defined as a separation of the ligand center of mass from the center of the FKBP binding site larger than 15 Å.
A rebinding event is defined as an unbinding event followed by a separation of the ligand/FKBP binding site smaller than 10 Å.
The binding affinity in the LIE model is approximated as the difference of the interaction energy of the ligand with two different surroundings, the protein and solvent in the bound state and only the solvent in the unbound state [50]. The LIE binding energy is calculated by averaging separately over all bound or unbound conformations using a cutoff of the intermolecular distance of 15 Å to discriminate between bound and unbound. The electrostatic energy term is multiplied by 0.5 to be consistent with the hydration energy of a single ion, which is equal to half the corresponding ion-water interaction energy [54]. The van der Waals energy term is multiplied by an empirical parameter 0.56 which is derived from linear fitting using only the five neutral compounds. Each of the total sampling is divided into five blocks and the block averaging errors for both energy terms are given in the table.
The unbinding time 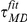 is
calculated by a single exponential fit of the cumulative distribution of
the unbinding events detected along the MD trajectories (see Fig. 5). The unbinding
time and error for each ligand are evaluated by single-exponential
fitting using 25 randomly selected MD runs out of 50, and calculating
the average error for the remaining 25 MD runs not used for the fitting,
i.e., the difference between the value predicted by the fitting curve
and the unbinding time measured along the MD trajectory. This procedure
is repeated 100 times for each ligand, and average values of unbinding
time and cross-validated error are reported in the table.
is
calculated by a single exponential fit of the cumulative distribution of
the unbinding events detected along the MD trajectories (see Fig. 5). The unbinding
time and error for each ligand are evaluated by single-exponential
fitting using 25 randomly selected MD runs out of 50, and calculating
the average error for the remaining 25 MD runs not used for the fitting,
i.e., the difference between the value predicted by the fitting curve
and the unbinding time measured along the MD trajectory. This procedure
is repeated 100 times for each ligand, and average values of unbinding
time and cross-validated error are reported in the table.
Measured by a fluorescence assay [30].
