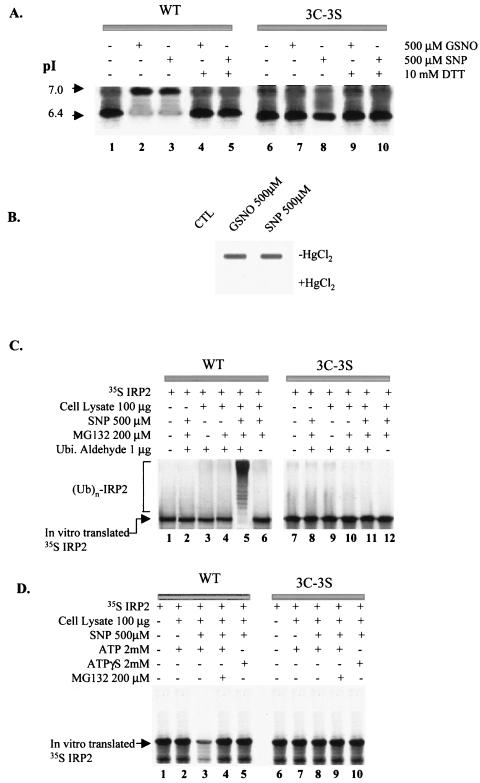
FIG. 2.
In vitro modification of IRP2 by SNP. (A) Isoelectric focusing analysis for S-nitrosylation of IRP2 and identification of target cysteines. Following treatment of in vitro-translated [35S]IRP2 with either 500 μM GSNO or SNP for 30 min, some samples (lanes 4, 5, 9, and 10) were treated with 10 mM DTT for an additional 5 min. Iodoacetate (35 mM) was added to protect sulfhydryls and to increase the negative charge on the unmodified thiol groups by its alkylation. The protein was subjected to isoelectric focusing and detected by autofluorography. (B) In vitro S-nitrosylation of recombinant WT IRP2. Recombinant IRP2 was treated without (control [CTL]) or with 500 μM concentration of either GSNO or SNP for 30 min. Following this treatment, the samples were treated without or with HgCl2 for 5 min and analyzed by slot blotting with anti-SNO antibody (Alexis Biochemicals Inc.). (C) In vitro ubiquitin conjugation assay of IRP2. In vitro-translated [35S]IRP2 was treated with or without 500 μM SNP for 30 min and then incubated (for 1.5 h) with cell lysate prepared from RAW 264.7 cells and various reagents as indicated. (D) In vitro degradation assay. In vitro-translated IRP2 was pretreated with 500 μM SNP for 30 min and incubated without or with cell lysate from RAW264.7 cells and other reagents as indicated.