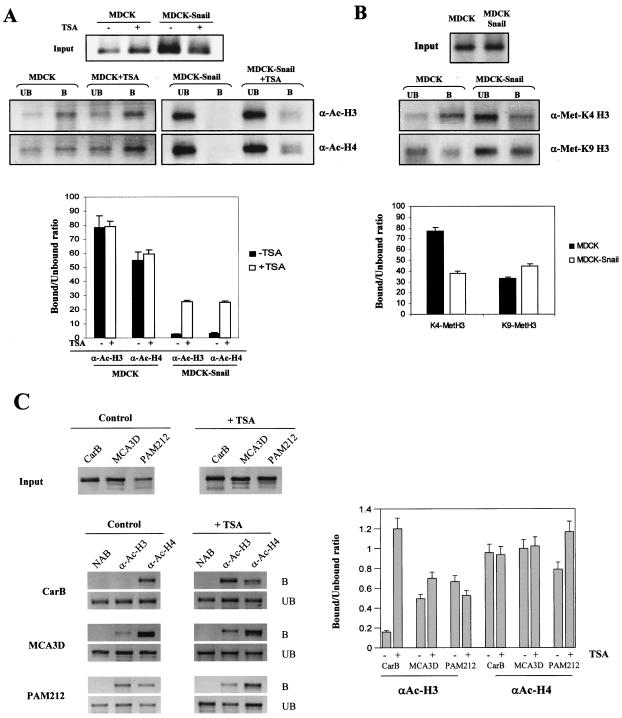
FIG. 2.
Histone acetylation and methylation analysis at the endogenous E-cadherin promoter in Snail-expressing and Snail-deficient cells. (A and B) ChIP analysis of the modification status of histones H3 and H4 at the endogenous E-cadherin promoter in MDCK-CMV (MDCK) and MDCK-Snail cells, with anti-acetyl-histone H3 (α-Ac-H3) and anti-acetyl-histone H4 (α-Ac-H4) and anti-dimethyl-K4 histone H3 (α-Met-K4-H3) and anti-dimethyl-K9 histone H3 (α-Met-K9-H3) antibodies. Where indicated, cells were treated with TSA (300 nM) for 24 h before formaldehyde cross-linking. The amplified dog E-cadherin promoter sequences in the input and the immunoprecitated bound and unbound fractions are shown in the upper panels. (C) ChIP assays of the histone H3 and H4 acetylation status at the endogenous E-cadherin promoter in mouse keratinocyte MCA3D, Pam212, and spindle CarB cells, with anti-acetyl-histone H3 (α-Ac-H3) and anti-acetyl-histone H4 (α-Ac-H4) antibodies. Where indicated, cells were treated with TSA (300 nM) for 24 h before formaldehyde cross-linking. The amplified mouse E-cadherin promoter sequences in the input (upper panels) and bound and unbound (lower panels) fractions are shown. Results from controls with no antibody (NAB), in which no amplification occurs, are also included for each cell line. Quantification of the amplified sequences in the immunoprecipitated fractions (represented as the ratio of bound to unbound fractions) with each antibody and corresponding cells lines and treatments is shown in the lower (A and B) and right (C) panels. Results represent the averages ± standard deviations of at least two experiments. B, bound; UB, unbound.