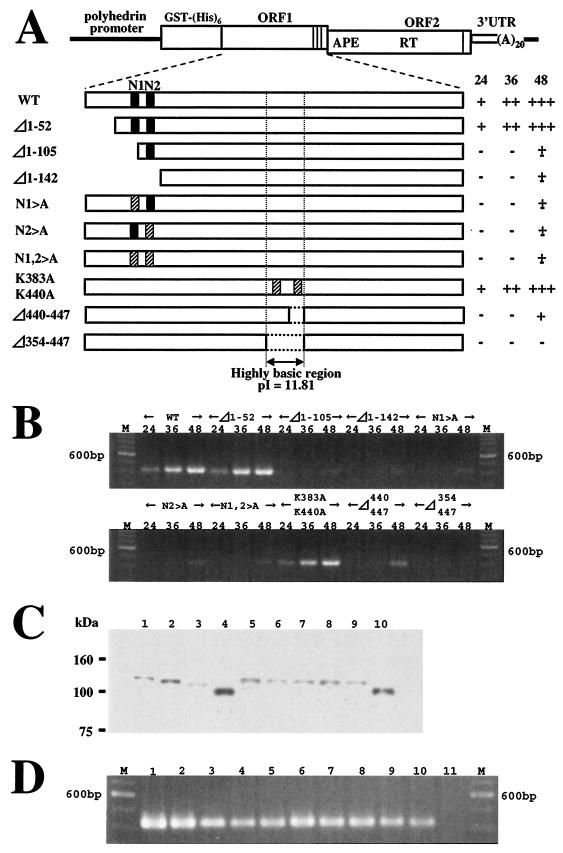
FIG. 7.
Retrotransposition activity of SART1 with mutations in the N-terminal and central regions of ORF1. (A) Constructs of various SART1 mutants. WT and mutated SART1 ORF1, ORF2, and 3′ untranslated region (UTR) were expressed downstream from the GST-His6 tag by AcNPV-recombinant virus infection of Sf9 cells. Closed boxes indicate putative NLSs. Hatched boxes indicate the substituted regions where several amino acids were replaced by alanine. In constructs N1>A, N2>A, and N1,2>A, RRKR in N1 and KRGR in N2 were replaced with AAAA. The K residues at 383 (K383A) and 440 (K440A) were replaced with A. The results of the in vivo retrotransposition assay (see panel B) are summarized on the right. The numbers at the top represent hpi. +++, very strong signal; ++, strong signal; +, weak signal; ±, very weak signal; −, no signal. (B) PCR amplification of the 3′ junctions of the retrotransposed WT SART1 or various mutants. The PCR band, which represents the SART1 retrotransposition, is 423 bp in length. (C) Western blots of mutant proteins. Protein production in mutants was analyzed by immunoblot assay with anti-His6 antiserum to detect His-tagged proteins. Lanes: 1, WT SART1; 2, Δ1-52; 3, Δ1-105; 4, Δ1-142; 5, N1>A; 6, N2>A; 7, N1,2>A; 8, K383,440A; 9, Δ440-447; 10, Δ353-447. (D) Rescue of mutant constructs by trans-complementation. At 36 h after coinfection of AcNPV viruses expressing various mutants with a construct producing only SART1 ORF1 (ORF1pWT), Sf9 genomic DNA was extracted and assayed by PCR detection (see Fig. 5B). Lanes: M, size marker (100-base ladder); 1, WT SART1; 2, Δ1-52 plus ORF1pWT; 3, Δ1-105 plus ORF1pWT; 4, Δ1-142 plus ORF1pWT; 5, N1>A plus ORF1pWT; 6, N2>A plus ORF1pWT; 7, N1,2>A plus ORF1pWT; 8, K383,440A plus ORF1pWT; 9, Δ440-447 plus ORF1pWT; 10, Δ353-447 plus ORF1pWT; 11, ORF1pWT.